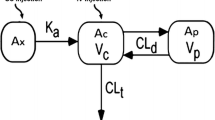
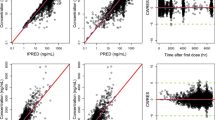
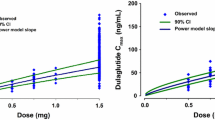
Summary
The article reviews the effect of diabetes on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs in humans.
For most drugs which cross the gastrointestinal wall by passive diffusion, oral absorption is unlikely to be affected by diabetes, although a delay in the absorption of tolazamide and a decrease in the extent of absorption of ampicillin have been reported. Subcutaneous absorption of insulin is more rapid in diabetic patients, whereas the intramuscular absorption of several drugs is slower.
The binding of a number of drugs in the blood is reduced in diabetes, which may be due to glycosylation of plasma proteins or displacement by plasma free fatty acids, the level of which is increased in diabetic patients. Plasma concentrations of albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein do not appear to be changed by the disease. The distribution of drugs with little or no binding in the blood is generally not altered, although the volume of distribution of phenazone (antipyrine) is reduced by 20% in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM).
In contrast to animal studies, the metabolic clearance of most drugs in humans appears to be unaffected or slightly reduced by the disease. The presence of fatty liver in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) may contribute to a reduced hepatic clearance, whereas decreased binding in the blood may cause an increase in clearance. The effect of diabetes on hepatic blood flow in humans appears to be unknown.
Diabetes affects kidney function in a significant number of diabetic patients. During the first 10 years after the onset of the disease, glomerular filtration is elevated in these patients. Thus, the renal clearance of a number of antibiotics has been shown to be increased in diabetic children. As the disease progresses, renal function is impaired and glomerular function declines from the initial elevated state. In diabetic adults the renal clearance of drugs either is comparable with that found in nondiabetic individuals or is reduced.
A limited number of studies have been conducted comparing the dose-response of cardiovascular drugs in diabetic patients with that in nondiabetic controls. Decreased, increased and unchanged responses have been reported. It is apparent that in some cases an altered response may be observed for a drug when administered to a diabetic patient compared with a similar nondiabetic individual. At the present time, it is not possible to ascertain whether these studies reflect true pharmacodynamic changes or merely alterations in pharmacokinetics.
It appears from the limited data available that significant, although perhaps not dramatic, changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics do occur as a result of diabetes. Because of the prevalence of the disease and the associated serious complications, further study is warranted on the effects of diabetes on both pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adithan C, Danda D, Swaminathan RP, Indhiresan J, Shashindran CH, et al. Effect of diabetes on salivary paracetamol elimination. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 15: 465–471, 1988a
Adithan C, Danda D, Swaminathan RP, Indhiresan J, Shashindran CH, et al. Effect of type I diabetes mellitus on theophylline elimination. Medical Science Research 16: 427–428, 1988b
Adithan C, Sriram G, Swaminathan RP, Krishnan M, Bapna JS, et al. Effect of type II diabetes mellitus on theophylline elimination. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy and Toxicology 27: 258–260, 1989a
Adithan C, Sriram G, Swaminathan RP, Shashindran CH, Bapna JS, et al. Differential effect of type I and type II diabetes mellitus on serum ampicillin levels. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy and Toxicology 27: 493–498, 1989b
Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T. Diabetic nephropathy in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes: an epidemiological study. Diabetologia 25: 496–501, 1983
Baba T, Tomiyama T, Murabayashi S, Tomiyama M, Takebe K. Enalapril pharmacokinetics in diabetic patients. Lancet 1: 226–227, 1989
Barry MG, Collins WCJ, Feely J. Plasma protein binding of drugs in insulin-dependent diabetes. British Journal of Pharmacology 89: 719P, 1986
Bechtel YC, Joanne C, Grandmottet M, Bechtel PR. The influence of insulin-dependent diabetes on the metabolism of caffeine and the expression of the debrisoquin oxidation phenotype. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 44: 408–417, 1988
Berlin I, Grimaldi A, Bosquet F, Puech AJ. Decreased beta-adrenergic sensitivity in insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 63: 262–265, 1986
Bodansky HJ, Drury PL, Cudworth AG, Evans DAP. Acetylator phenotypes and type I (insulin-dependent) diabetics with microvascular disease. Diabetes 30: 907–910, 1981
Brownlee M, Cerami A, Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. New England Journal of Medicine 318: 1315–1321, 1988
Burrows AW, Hockaday TDR, Mann JI, Taylor JG. Diabetic dimorphism according to acetylator status. British Medical Journal 1: 208–210, 1978
Chase PH, Glasgow AM. Juvenile diabetes mellitus and serum lipids and lipoprotein levels. American Journal of Diseases of Children 130: 1113–1117, 1976
Daintith H, Stevenson IH, O’Malley K. Influence of diabetes mellitus on drug metabolism in man. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 13: 55–58, 1976
Dajani RM, Kayyali S, Saheb SE, Birbari A. A study on the physiological disposition of acetophenetidin by the diabetic man. Comparative and General Pharmacology 5: 1–9, 1974
Damsgaard EM. Why do elderly diabetics burden the health care system more than non-diabetics? Danish Medical Bulletin 36: 89–92, 1989
Della-Coletta AA, Eller MG. The bioavailability of tolazamide in diabetic patients and healthy subjects. Abstract no. PP 1301. Pharmaceutical Research 5: S–174, 1988
Evans DAP. N-acetyltransferase. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 42: 157–234, 1989
Evans DAP, Paterson S, Francisco P, Alvarez G. The acetylator phenotypes of Saudi Arabian diabetics. Journal of Medical Genetics 22: 479–483, 1985
Fass RJ, Saslaw S. Clindamycin: clinical and laboratory evaluation of parenteral therapy. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 263: 369–382, 1972
Favreau LV, Schenkman JB. Composition changes in hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 during onset of streptozocin-induced diabetes and during insulin treament. Diabetes 37: 577–584, 1988
Feldman M, Schiller LR. Disorders of gastrointestinal motility associated with diabetes mellitus. Annals of Internal Medicine 98: 378–384, 1983
Foster KJ, Griffith AH, Dewbury K, Price CP, Wright R. Liver disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. Postgraduate Medical Journal 56: 767–772, 1980
Fraze E, Donner CC, Swislocki ALM, Chiou Y-AM, Chen Y-DI, et al. Ambient plasma free fatty acid concentrations in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: evidence for insulin resistance. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 61: 807–811, 1985
Fuccella LM, Tamassia V, Valzelli G. Metabolism and kinetics of the hypoglycemic agent glipizide in man — comparison with glibenclamide. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 13: 68–75, 1973
Garcia G, de Vidal EL, Trujillo H. Serum levels and urinary concentrations of kanamicin, bekanamicin and amikacin (BB-K8) in diabetic children and a control group. Journal of International Medical Research 5: 322–329, 1977
Gatti G, Crema F, Attardo-Parrinello G, Fratino P, Aguzzi F, et al. Serum protein binding of Phenytoin and valproic acid in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 9: 389–391, 1987
Gibaldi M. Biopharmaceutics and clinical pharmacokinetics, 3rd ed., pp. 206–227, Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1984
Gibaldi M, Perrier D. Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., p. 200, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982
Grainger-Rousseau T-J, McElnay JC, Collier PS. The influence of disease on plasma protein binding of drugs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 54: 1–13, 1989
Grasela DM, Wender RC, Ballas SK, Rocci ML. The effect of diabetes and sickle cell anemia on the drug metabolizing activity of erythrocyte ketone reductases. Abstract no. IIIB-2. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 45: 180, 1989
Gundersen HJG. Peripheral blood flow and metabolic control in juvenile diabetes. Diabetologia 10: 225–231, 1974
Haggendal E, Steen B, Svanborg A. Blood flow in subcutaneous fat tissue in patients with diabetes mellitus. Acta Medica Scandinavica 187: 49–53, 1970
Harris MI. Prevalence of noninsulin-dependent diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. In Harris & Hamman (Eds) Diabetes in America, NIH Publication no. 85-1468, p. VI–1, 1985
Hildebrandt P, Birch K, Nielsen SL, Sestoft L. Absorption of infused insulin: kinetics and relation to subcutaneous blood flow. Abstract no. 171. Diabetologia 25: 164, 1983
Hildebrandt P, Birch K, Sestoft L, Nielsen SL. Non-linear relationship between subcutaneous blood flow and insulin absorption. Abstract no. 134. Diabetologia 23: 174, 1982
Isacson D, Stalhammar J. Prescription drug use among diabetics — a population study. Journal of Chronic Diseases 40: 651–660, 1987
Jungmann E, Seel K, Hofmann E, Scheuermann E-H, Schoffling K. Effects of nifedipine on renal responses to human atrial natriuretic peptide in healthy subjects and normoglycemic patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Klinische Wochenschrift 67: 1174–1181, 1989
Jungmann E, Walter-Schrader M-C, Haak T, Fassbinder W, Wambach G, et al. Impaired renal responsiveness to human atrial natriuretic peptide (hANP) in normotensive patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Klinische Wochenschrift 66: 527–532, 1988
Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. American Journal of Cardiology 34: 29–34, 1974
Kazumi T, Yoshino G, Okutani T, Kato J, Kasama T, et al. Plasma lipoprotein and apolipoprotein concentrations and glycemic control during short-term treatment with nifedipine in hypertensive patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Current Therapeutic Research 46: 951–958, 1989
Kearns GL, Kemp SF, Turley CP, Nelson DL. Protein binding of Phenytoin and lidocaine in pediatric patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 11: 14–23, 1988
Kemp SF, Kearns GL, Turley CP. Alteration of phenytoin binding by glycosylation of albumin in IDDM. Diabetes 36: 505–509, 1987
Klein R, Klein BEK. Vision disorders in diabetes. In Harris & Hamman (Eds) Diabetes in America, NIH Publication no. 85-1468, p. XIII–1, 1985
Koldendorf K, Bojsen J, Nielsen SL. Adipose tissue blood flow and insulin disappearance from subcutaneous tissue. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 25: 598–604, 1979
Krolewski AS, Warram JH, Rand LI, Kahn CR. Epidemiologic approach to the etiology of type I diabetes mellitus and its complications. New England Journal of Medicine 317: 1390–1398, 1987
Ladero JM, Arrojo A, de Salamanca RE, Gomez M, Cano F, et al. Hepatic acetylator phenotype in diabetes mellitus. Annals of Clinical Research 14: 187–189, 1982
Lauritzen T, Binder C, Faber OK. Importance of insulin absorption, subcutaneous blood flow and residual beta-cell function in insulin therapy. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 283 (Suppl.): 81–85, 1980
Leinonen H, Matikainen E, Juntunen J. Permeability and morphology of skeletal muscle capillaries in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 22: 158–162, 1982
Lerner PI, Weinstein L. Abnormalities of absorption of benzyl-penicillin G and sulfisoxazole in patients with diabetes mellitus. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 248: 37–51, 1964
Lloyd-Mostyn RH, Watkins PJ. Defective innervation of heart in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. British Medical Journal 3: 15–17, 1975
Longhurst PA, LaCagnin LB, Staats DA, Colby HD. Changes in hepatic drug metabolism in alloxan-diabetic male rabbits. Biochemical Pharmacology 35: 1768–1771, 1986
Lucas PD, Foy JM. Effects of experimental diabetes and genetic obesity on regional blood flow in the rat. Diabetes 26: 786–792, 1977
Madacsy L, Bokor M, Kozocsa G. Carbenicillin half-life in children with early diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 14: 155–158, 1976
Madacsy L, Bokor M, Matusovits L. Penicillin clearance in diabetic children. Acta Paediatrica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae 16: 139–142, 1975
Mattila MJ, Tiitnen H. The rate of isoniazid inactivation in Finnish diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Annales Academiae Scientiarum Fennicae 45: 423–427, 1967
McLaren EH, Burden AC, Moorhead PJ. Acetylator phenotypes in diabetic neuropathy. British Medical Journal 2: 291–293, 1977
McNamara PJ, Blouin RA, Brazzell RK. The protein binding of phenytoin, propranolol, diazepam and AL01576 (an aldose reductase inhibitor) in human and rat diabetic serum. Pharmaceutical Research 5: 261–265, 1988
Mereish KA, Rosenberg H, Cobby J. Glucosylated albumin and its influence on salicylate binding. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 71: 235–238, 1982
Mogensen CE, Andersen MJF. Increased kidney size and glomerular filtration rate in early juvenile diabetes. Diabetes 22: 706–712, 1973
Mogensen CE, Christensen CK, Vittinghus E. The stages in diabetic renal disease with emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 32 (Suppl. 2): 64–78, 1983
Moore EW, Mitchell ML, Chalmers TC. Variability in absorption of insulin-I(131) in normal and diabetic subjects after subcutaneous and intramuscular injection. Journal of Clinical Investigation 38: 1222–1227, 1959
Murali KV, Adithan C, Shashindran CH, Gambhir SS, Chandrasekar S. Antipyrine metabolism in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 10: 7–13, 1983
Narang APS, Dutta DV, Khare AK. Impairment of drug clearance in patients with diabetes mellitus and liver cirrhosis. Indian Journal of Medical Research 85: 321–325, 1987
Nishio Y, Kashiwagi A, Terada M, Kida Y, Hatanaka I, et al. The effect of cardiac contractile response to epinephrine infusion in subjects with diabetes mellitus. In Shigeta et al. (Eds) Best approach to the ideal therapy of diabetes mellitus, pp. 459–462, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1987
Nosadini R, De Kreutzenberg S, Duner E, Iori E, Avogaro A, et al. Porcine and human insulin absorption from subcutaneous tissues in normal and insulin-dependent diabetic subjects: a deconvolution based approach. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 67: 551–559, 1988
O’Byrne S, O’Connor P, Feely J. Plasma protein binding of lignocaine and warfarin in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26: 648P, 1988
O’Connell ME, Awni WM, Goodman M, Cass O, Melikian AP, et al. Bioavailability and disposition of metoclopramide after single- and multiple-dose administration in diabetic patients with gastroparesis. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 610–614, 1987
O’Connor P, Feely J. Clinical pharmacokinetics and endocrine disorders: therapeutic implications. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 13: 345–364, 1987
Ordonez JD, Hiatt RA. Comparison of type II and type I diabetics treated for end-stage renal disease in a large prepaid health plan population. Nephron 51: 524–529, 1989
Packer M, Lee WH, Medina N, Yushak M, Kessler PD, et al. Influence of diabetes mellitus on changes in left ventricular performance and renal function produced by converting enzyme inhibition in patients with severe chronic heart failure. American Journal of Medicine 82: 1119–1126, 1987
Palumbo PJ, Melton LJ. Peripheral vascular disease and diabetes. In Harris & Hamman (Eds) Diabetes in America, NIH Publication no. 85-1468, p. XV–1, 1985
Pirttiaho HI, Salmela PI, Sotaniemi EA, Pelkonen RO, Pitkanen U, et al. Drug metabolism in diabetic subjects with fatty livers. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 895–899, 1984
Rao GMM, Morghom LO, Abukhris AA. Serum beta-glycosidases in diabetes mellitus. Clinical Physiology and Biochemistry 7: 161–164, 1989
Reinke LA, Stohs SJ, Rosenberg H. Increased aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in hepatic microsomes from streptozotocin-diabetic female rats. Xenobiotica 8: 769–778, 1979
Rendell M, Lassek WD, Ross DA, Smith C, Kernek S, et al. A pharmaceutical profile of diabetic patients. Journal of Chronic Diseases 36: 193–202, 1983
Ruiz-Cabello F, Erill S. Abnormal serum protein binding of acidic drugs in diabetes mellitus. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 36: 691–695, 1984
Salmela PI, Sotaniemi EA, Pelkonen RO. The evaluation of the drug-metabolizing capacity in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 29: 788–794, 1980
Scott AK, Cameron GA, Khir ASM, McHardy KC, Hawksworth GM. Oxazepam elimination in patients with diabetes mellitus. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26: 224P, 1988
Self TH, Hood J, Miller ST. Diabetes mellitus and the hypoprothrombinemic response to warfarin. Journal of the American Medical Association 239: 2239, 1978
Shenfield GM, McCann VJ, Tjokresetio R. Acetylator status and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 22: 441–444, 1982
Stafford WL. Abnormality in the binding of an organic anion by diabetic serum. Lancet 1: 243–245, 1962
Sugimoto T, Rosansky SJ. The incidence of treated end stage renal disease in the eastern United States: 1973–1979. American Journal of Public Health 74: 14–17, 1984
Sugiyama H, Nakajo Y, Miyano T, Tanaka A, Uchimura I, et al. Cardiovascular reactivity and plasma renin responses to isoproterenol in diabetics with autonomic neuropathy. In Sakamoto et al. (Eds) Current topics in clinical and experimental aspects of diabetes mellitus, pp. 323–327, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1985
Terada M, Yasuda H, Kashawagi A, Nishio Y, Hatanaka I, et al. Sympathetic nerve dysfunction and increased heart rate response to epinephrine in diabetic patients. In Shigeta et al. (Eds) Best approach to the ideal therapy of diabetes mellitus, pp. 497–500, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1987
Ueda H, Sakurai T, Ota M, Nakajima A, Kamii K, et al. Disappearance rate of tolbutamide in normal subjects and in diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease. Diabetes 12: 414–419, 1963
Wahlin-Boll E, Aimer LO, Melander A. Bioavailability, pharmacokinetics and effects of glipizide in type II diabetics. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 7: 363–372, 1982
Weinstein L, Meade RH. Absorption and excretion of penicillin injected into the muscles of patients with diabetes mellitus. Nature 192: 987–988, 1961
Wiseman MJ, Saunders AJ, Keen H, Viberti G. Effect of blood glucose control on increased glomerular filtration rate and kidney size in insulin-dependent diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 312: 617–621, 1985
Yee GC, Evans WE. Reappraisal of guidelines for pharmacokinetic monitoring of aminoglycosides. Pharmacotherapy 1: 55–74, 1981
Zysset T, Weitholtz H. Differential effect of type I and type II diabetes on antipyrine disposition in man. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 34: 369–375, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gwilt, P.R., Nahhas, R.R. & Tracewell, W.G. The Effects of Diabetes Mellitus on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 20, 477–490 (1991). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199120060-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199120060-00004