Abstract
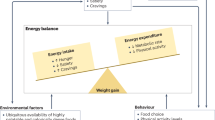
The increased prevalence of obesity in childhood and adolescence highlights the need for effective treatment approaches. Initial assessments of these patients should include taking a careful history (investigating comorbidities, family history and potentially modifiable behaviors) and physical examination with BMI plotted on a BMI-for-age chart. The degree of investigation is dependent on the patient's age and severity of obesity, the findings on history and physical examination, and associated familial risk factors. There are several broad principles of conventional management: management of comorbidities; family involvement; taking a developmentally appropriate approach; the use of a range of behavior change techniques; long-term dietary change; increased physical activity; and decreased sedentary behaviors. Orlistat can be useful as an adjunct to lifestyle changes in severely obese adolescents and metformin can be used in older children and adolescents with clinical insulin resistance. Bariatric surgery should be considered in those who are severely obese, with recognition of the need for management in centers with multidisciplinary weight management teams and for surgery to be performed in tertiary institutions experienced in bariatric surgery. Finally, given the high prevalence and chronic nature of obesity, coordinated models of care for health-service delivery for the management of pediatric obesity are needed.
Key Points
-
BMI (weight/height2) should be plotted routinely on a BMI-for-age chart and provides a reasonable measure of body fatness in children and adolescents with obesity
-
Conventional management for childhood and adolescent obesity includes: management of comorbidities; family involvement; developmentally appropriate approaches; behavior change techniques; long-term dietary change; increased physical activity; and decreased sedentary behaviors
-
Pharmacotherapy for obesity is limited; orlistat can be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes in severely obese adolescents, while metformin can be used in older children and adolescents with clinical insulin resistance
-
Bariatric surgery should be considered in severely obese adolescents, preferably with management in centers with multidisciplinary weight management teams and surgery performed in tertiary institutions experienced in bariatric surgery
-
Coordinated models of care for health-service delivery for the management of pediatric obesity are needed
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Y. & Lobstein, T. Worldwide trends in childhood overweight and obesity. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 1, 11–25 (2006).
Lobstein, T., Baur, L. & Uauy, R. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes. Rev. 5, 4–104 (2004).
International Obesity TaskForce. Obesity prevalence worldwide. International Association for the Study of Obesity [online], (2011).
de Onis, M., Blossner, M. & Borghi, E. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 92, 1257–1264, (2010).
Rokholm, B., Baker, J. L. & Sørenson, T. I. A. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999—a review of evidence and perspectives. Obes. Rev. 11, 835–846 (2010).
Daniels, S. R. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. (London) 33 (Suppl. 1), S60–S65 (2009).
Han, J. C., Lawlor, D. A. & Kimm, S. Y. S. Childhood obesity. Lancet 375, 737–748 (2010).
Benson, L., Baer, H. J. & Kaelber, D. C. Trends in the diagnosis of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: 1999–2007. Pediatrics 123, e153–e158 (2009).
Cretikos, M. A., Valenti, L., Britt, H. C. & Baur, L. A. General practice management of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents in Australia. Med. Care 4, 1163–1169 (2008).
O'Connor, J., Youde, L. S., Allen, J. R. & Baur, L. A. Obesity and under-nutrition in a tertiary paediatric hospital. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 40, 299–304 (2004).
Woo, J. G., Zeller, M. H., Wilson, K. & Inge, T. Obesity identified by discharge ICD-9 codes underestimates the true prevalence of obesity in hospitalized children. J. Pediatr. 154, 327–331 (2009).
Barlow, S.E. ; Expert Committee. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Pediatrics 120 (Suppl. 4), S164–S192 (2007).
Krebs, N. F., Himes, J. H., Jacobson, D., Nicklas, T. A., Guilday, P. & Styne, D. Assessment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics 120 (Suppl. 4), S193–S228 (2007).
National Health and Medical Research Council. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. Australian govemernment Department of Health [online], (2003).
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Management of obesity: a national clinical guideline. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network [online], (2010).
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Obesity: guidance on the prevention, identification, assessment and management of overweight and obesity in adults and children. National Health Service National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence [online], (2011).
Hand, B. P. et al. The associations between physical activity, screen time and weight from 6 to 14 yrs: the Raine Study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 14, 397–403 (2011).
Mei, Z. et al. Validity of body mass index compared with other body-composition screening indexes for the assessment of body fatness in children and adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 75, 978–985 (2002).
Freedman, D. S. et al. Classification of body fatness by body mass index-for-age categories among children. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 163, 805–811 (2009).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Clinical growth charts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [online], (2011).
McCarthy, H. D. Body fat measurements in children as predictors for the metabolic syndrome: focus on waist circumference. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 65, 385–392 (2006).
McCarthy, H. D., Jarrett, K. V. &, Crawley, H. F. The development of waist circumference percentiles in British children aged 5.0–169 y. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 55, 902–907 (2001).
Fernandez, J. R., Redden, D. T., Pietrobelli, A. & Allison, D. B. Waist circumference percentiles in nationally representative samples of African-American, European-American, and Mexican-American children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. 145, 439–444 (2004).
Mokha, J. S. et al. Utility of waist-to-height ratio in assessing the status of central obesity and related cardiometabolic risk profile among normal weight and overweight/obese children: the Bogalusa Heart Study. BMC Pediatr. 10, 73 (2010).
Garnett, S. P., Baur, L. A. & Cowell, C. T. Waist to height ratio: a simple option for determining excess central adiposity in young people. Int. J. Obes. 32, 1028–1030 (2008).
McCrindle, B. W. Assessment and management of hypertension in children and adolescents. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 7, 155–163 (2010).
The National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114 (Suppl. 2), 555–576 (2004).
Higgins, S. P., Freemark, M. & Prose, N. S. Acanthosis nigricans: a practical approach to evaluation and management. Dermatol. Online J. 14, 2 (2008).
Singh, S. & Schwartz, R. A. Juvenile acanthosis nigricans. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 57, 502–508 (2007).
Reinehr, T. et al. Definable somatic disorders in overweight children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. 150, 618–622 (2007).
Farooqi, S. & O'Rahilly, S. Monogenic obesity in humans. Annu. Rev. Med. 56, 443–458 (2005).
Sabin, M. A., Werther, G. A. & Kiess, W. Genetics of obesity and overgrowth syndromes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 207–220 (2011).
Chevenne, D., Trivin, F. & Porquet, D. Insulin assays and reference values. Diabetes Metab. 26, 459–476 (1999).
Rönnemaa, T. et al. Serum insulin and other cardiovascular risk indicators in children, adolescents and young adults. Ann. Med. 23, 67–72 (1991).
Levers-Landis, C. E. & Redline, S. Pediatric sleep apnea: implications of the epidemic of childhood overweight. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 175, 436–461 (2007).
Toprak, D. et al. Adiposity in childhood is related to C-reactive protein and adiponectin in young adulthood: from the Bogalusa Heart Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19, 185–190 (2011).
Oude Luttikhuis, H. et al. Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. Issue 1. Art. No.: CD001872. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001872.pub2 (2009).
Reinehr, T. et al. Two-year follow-up in 21,784 overweight children and adolescents with lifestyle intervention. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17, 1196–1199 (2009).
Cosat, D. J. & Mitchell, R. Adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apniea in obese children: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 140, 455–460 (2009).
Daniels, S. R. & Greer, F. R. Lipid screening and cardiovascular health in childhood. Pediatrics 122, 198–208 (2008).
Lurbe, E. et al. Management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents: recommendations of the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 27, 1719–1742 (2009).
Lindbäck, S. M. et al. Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a comprehensive review. Adv. Pediatr. 57, 85–140 (2010).
Rosenbloom, A. L., Silverstein, J. H., Ameniya, S., Zeitler, P. & Klingensmith, G. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 10 (Suppl. 12), 117–132 (2009).
Dietz, W. H. & Robinson, T. N. Clinical practice. Overweight children and adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 2100–2109 (2005).
McLean, N., Griffin, S., Toney, K. & Hardeman, W. Family involvement in weight control, weight maintenance and weight-loss interventions: a systematic review of randomised trials. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 27, 987–1005 (2003).
Epstein, L. H., Valoski, A., Wing, R. R. & McCurley, J. Ten-year follow-up of behavioral, family-based treatment for obese children. JAMA 264, 2519–2523 (1990).
Nuutinen, O. & Knip, M. Predictors of weight reduction in obese children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 46, 785–794 (1992).
Golan, M., Weizman, A., Apter, A. & Fainaru, M. Parents as the exclusive agents of change in the treatment of childhood obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 67, 1130–1135 (1998).
Nowicka, P. & Flodmark, C.-E. Family in pediatric obesity management: a literature review. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 3 (Suppl. 1), 44–50 (2008).
Young, K. M., Northern, J. J., Lister, K. M., Drummond, J. A. & O'Brien, W. H. A meta-analysis of family-behavioural weight-loss treatments for children. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 27, 240–249 (2007).
Shrewsbury, V. A., Steinbeck, K. S., Torvaldsen, S. & Baur, L. A. The role of parents in pre-adolescent and adolescent overweight and obesity treatment: a systematic review of clinical recommendations. Obes. Rev. http:dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-1789X.2011.00882.x.
Golan, M. & Crow, S. Targeting parents exclusively in the treatment of childhood obesity: long-term results. Obes. Res. 12, 357–361 (2004).
Epstein, L. H., Myers, M. D., Raynor, H. A. & Saelens, B. E. Treatment of pediatric obesity. Pediatrics 101, 554–570 (1998).
Brennan, L. et al. A cognitive behavioural intervention for overweight and obese adolescents illustrated by four case studies. Behav. Change 26, 190–213 (2009).
Saelens, B. E. & McGrath, A. M. Self-monitoring adherence and adolescent weight control efficacy. Child Health Care 32, 137–152 (2003).
Alm, M. E., Neumark-Sztainer, D., Story, M. & Boutelle, K. N. Self-weighing and weight control behaviors among adolescents with a history of overweight. J. Adolesc. Health 44, 424–430 (2009).
Miller, W. R. & Rollnick, S. Motivational interviewing: preparing people for change 2nd edn (Guildford Press, New York, 2002).
Carels, R. A. et al. Using motivational interviewing as a supplement to obesity treatment: a stepped care approach. Health Psychol. 26, 369–374 (2007).
Collins, C. E., Warren, J., Neve, M., McCoy, P. & Stokes, B. J. Measuring effectiveness of dietetic interventions in child obesity: a systematic review of randomized trials. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 160, 906–922 (2006).
Abete, I., Astrup, A., Martínez, J. A., Thorsdottir, I. & Zulet, M. A. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome: role of different dietary macronutrient distribution patterns and specific nutritional components on weight loss and maintenance. Nutr. Rev. 68, 214–231 (2010).
Hession, M., Rolland, C., Kulkarni, U., Wise, A. & Broom, J. Systematic review of randomized controlled trials of low-carbohydrate vs. low-fat/low-calorie diets in the management of obesity and its comorbidities. Obes. Rev. 10, 36–50 (2009).
Thomas, D. E., Elliott, E. J. & Baur, L. Low glycaemic index or low glycaemic load diets for overweight and obesity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. Issue 3. Art. No.: CD005105. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005105.pub2 (2007).
Papadaki, A. et al. The effect of protein and glycemic index on children's body composition: the DiOGenes randomized study. Pediatrics 126, E1143–E1152 (2010).
Larsen, T. M. et al. Diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index for weight-loss maintenance. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 2102–2113 (2010).
Whitaker, R. C. Obesity prevention in pediatric primary care: four behaviors to target. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 157, 725–727 (2003).
Fairburn, C. G., Welch, S. L., Doll, H. A., Davies, B. A. & O'Connor, M. E. Risk factors for bulimia nervosa: a community-based case-control study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 54, 509–517 (1997).
Patton, C. G., Selzer, R., Coffey, C., Carlin, J. B. & Wolfe, R. Onset of adolescent eating disorders: population-based cohort study over 3 years. BMJ 318, 765–768 (1999).
Butryn, M. I. & Wadden, T. A. Treatment of overweight in children and adolescents: does dieting increase the risk of eating disorders? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 37, 285–293 (2005).
Hill, A. J. Obesity and eating disorders. Obes. Rev. 8 (Suppl. 1), 151–155 (2007).
Epstein, L. H., Wing, R. R., Koeske, R. & Valoski, A. A comparison of lifestyle change and programmed exercise on weight and fitness changes in obese children. Behav. Ther. 13, 651–665 (1982).
Epstein, L. H., Valoski, A., Koeske, Wing, R. R. & McCurley, J. Ten year outcomes of behavioural family-based treatment for childhood obesity. Health Psychol. 13, 373–383 (1994).
Atlantis, E., Barnes, E. H. & Singh, M. A. Efficacy of exercise for treating overweight in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 30, 1027–1040 (2006).
Benson, A. C., Torode, M. E. & Fiatarone Singh, M. A. Effects of resistance training on metabolic fitness in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Obes. Rev. 9, 43–66 (2008).
Shaw, K., Gennat, H., O'Rourke, P. & Del Mar, C. Exercise for overweight or obesity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. Issue 4. Art. No.: CD003817 doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003817.pub3 (2006).
Epstein, L. H., Paluch, R. A., Gordy, C. C. & Dorn, J. Decreasing sedentary behaviors in treating pediatric obesity. Arch. Pediatr. Adol. Med. 154, 220–226 (2000).
Tsai, A. G. & Wadden, T. A. Systematic review: an evaluation of major commercial weight loss programs in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 142, 56–66 (2005).
Figueroa-Colon, R., von Almen, T. K., Franklin. F. A., Schuftan, C. & Suskind, R. M. Comparison of two hypocaloric diets in obese children. Am. J. Dis. Child. 147, 160–166 (1993).
Suskind, R. M. et al. Recent advances in the treatment of childhood obesity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 699, 181–199 (1993).
Widhalm, K. M. & Zwiauer, K. F. Metabolic effects of a very low calorie diet in obese children and adolescents with special reference to nitrogen balance. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 6, 467–474 (1987).
Sothern, M., Udall, J. N., Suskind, R. M., Vargas, A. & Blecker, U. Weight loss and growth velocity in obese children after very low calorie diet, exercise, and behavior modification. Acta Paediatr. 89, 1036–1043 (2002).
Sjöstrom, L. et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group. Lancet 352, 167–172 (1998).
Padwal, R. S., Rucker, D., Li, S. K., Curioni, C. & Lau, D. C. W. Long-term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. Issue 4. Art. No.: CD004094. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004094.pub2 (2004).
James, W. P. et al. Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 905–917 (2010).
Chanoine, J., Hampl, S., Jensen, C., Boldrin, M. & Hauptman, J. Effect of orlistat on weight and body composition in obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 293, 2873–2883 (2005).
Maahs, D. et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss in adolescents. Endocr. Pract. 12, 18–28 (2006).
Ozkan, B., Bereket, A., Turan, S. & Keskin, S. Addition of orlistat to conventional treatment in adolescents with severe obesity. Eur. J. Paediatr. 163, 738–7341 (2004).
Quinn, S. M., Garnett, S. P., Cowell, C. T. & Baur, L. A. Treatment of clinical insulin resistance in children: a systematic review. Obes. Rev. 11, 722–730 (2009).
Srinivasan, S. et al. Randomised controlled trial of metformin for obesity and insulin resistance in children and adolescents: improvement in body composition and fasting insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, 2074–2080 (2006).
Love-Osborne, K., Sheeder, J. & Zeitler, P. Addition of metformin to a lifestyle modification program in adolescents with insulin resistance. J. Paediatr. 152, 817–822 (2008).
Atabek, M. E. & Pirgon, O. Use of metformin in obese adolescents with hyperinsulinemia: a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 21, 339–348 (2008).
Wilson, D. M. et al. Metformin extended release treatment of adolescent obesity. Arch. Pediatr. Adol. Med. 164, 116–123 (2010).
Yanovski, J. A. et al. Effects of metformin on body weight and body composition in obese insulin-resistant children. Diabetes 60, 477–485 (2011).
Wald, A. B. & Uli, N. K. Pharmacotherapy in pediatric obesity: current agents and future directions. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 10, 205–214 (2009).
Colquitt, J. L., Picot, J., Loveman, E. & Clegg, A. J. Surgery for obesity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. Issue 2. Art. No.: CD003641. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003641.pub3 (2009).
O'Brien, P. E. et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in severely obese adolescents: a randomized trial. JAMA 303, 519–526 (2010).
Treadwell, J. R., Sun, F. & Schoelles, K. Systematic review and meta-analysis of bariatric surgery for pediatric obesity. Ann. Surg. 248, 763–776 (2008).
Baur, L. A. & Fitzgerald, D. A. Recommendations for bariatric surgery in adolescents in Australia and New Zealand. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 46, 704–707 (2010).
Inge, T. H. et al. Bariatric surgery for severely overweight adolescents: concerns and recommendations. Pediatrics 114, 217–223 (2004).
August, G. P. et al. Prevention and treatment of pediatric obesity: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline based on expert opinion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 4576–4599 (2008).
Magarey, A. M. et al. A parent-led family-focused treatment program for overweight 5–9 year olds: the PEACH RCT. Pediatrics 127, 214–222 (2011).
Collins, C. E. et al. Parent diet modification, child activity or both in obese children: an RCT. Pediatrics 127, 619–627 (2011).
Wilfley, D. E. et al. Efficacy of maintenance treatment approaches for childhood overweight: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 298, 1661–1673 (2007).
Feachem, R. G., Sekhri, N. K. & White, K. L. Getting more for their dollar: a comparison of the NHS with California's Kaiser Permanente. BMJ 324, 135–141 (2002).
Department of Health publications and policy guidance. Supporting people with long term health conditions. Department of Health Publications [online], (2007).
Acknowledgements
V. Shrewsbury was supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Postgraduate Research Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contibuted equally to all aspects of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baur, L., Hazelton, B. & Shrewsbury, V. Assessment and management of obesity in childhood and adolescence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8, 635–645 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.165
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.165
This article is cited by
-
Scoping literature review and focus groups with healthcare professionals on psychosocial and lifestyle assessments for childhood obesity care
BMC Health Services Research (2023)
-
The acceptability, effectiveness, and impact of different models of care for pediatric weight management services: protocol for a concurrent mixed-methods study
BMC Health Services Research (2018)
-
Tip60-mediated lipin 1 acetylation and ER translocation determine triacylglycerol synthesis rate
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Treatment of adolescent obesity
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2018)
-
Metformin for Weight Gain Associated with Second-Generation Antipsychotics in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
CNS Drugs (2018)