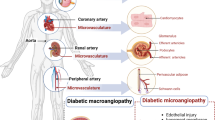
Abstract
The morbidity and mortality of diabetes mellitus are mostly attributed to cardiovascular complications. Despite tremendous advancement in glycemic control, anti-diabetic medications have failed to revert vascular impairment once triggered by the metabolic disorder. The angiogenic growth factors, Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) and Angiopoietin-2 (Ang2), are crucial regulators of vessel formation and maintenance starting with embryonic development and continuing through life. In mature vessels, angiopoietins control vascular permeability, inflammation and remodeling. A crucial role of angiopoietins is to drive vascular inflammation from the active to the quiescent state, enabling restoration of tissue homeostasis. The mechanism is of particular importance for healing and repair after damage, two conditions typically impaired in metabolic disorders. There is an emerging body of evidences suggesting that the imbalance of Ang1 and Ang2 regulation, leading to an increased Ang2/Ang1 ratio, represents a culprit of the vascular alterations of patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacological modulation of Ang1 or Ang2 actions may help prevent or delay the onset of diabetic vascular complications by restoring vessel function, favoring tissue repair and maintaining endothelial quiescence. In this review, we present a summary of the role of Ang1 and Ang2, their involvement in diabetic complications, and novel therapeutic strategies targeting angiopoietins to ameliorate vascular health in metabolic disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438(7070):932–936. doi:10.1038/nature04478
Folkman J (2003) Fundamental concepts of the angiogenic process. Curr Mol Med 3(7):643–651
Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Acheson A, Compton DL, Jain V, Ryan TE, Bruno J, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD (1996) Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell 87(7):1161–1169
Papapetropoulos A, Garcia-Cardena G, Dengler TJ, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD, Sessa WC (1999) Direct actions of angiopoietin-1 on human endothelium: evidence for network stabilization, cell survival, and interaction with other angiogenic growth factors. Lab Invest J Tech Methods Pathol 79(2):213–223
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopoulos N, Daly TJ, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1997) Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277(5322):55–60
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, Boland P, Alexander CR, Zagzag D, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ (1999) Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 284(5422):1994–1998
Simons M (2005) Angiogenesis, arteriogenesis, and diabetes: paradigm reassessed? J Am Coll Cardiol 46(5):835–837. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.06.008
Abaci A, Oguzhan A, Kahraman S, Eryol NK, Unal S, Arinc H, Ergin A (1999) Effect of diabetes mellitus on formation of coronary collateral vessels. Circulation 99(17):2239–2242
Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M (2014) Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med 6(265):265–266. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3009337
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1996) Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 87(7):1171–1180
Jeansson M, Gawlik A, Anderson G, Li C, Kerjaschki D, Henkelman M, Quaggin SE (2011) Angiopoietin-1 is essential in mouse vasculature during development and in response to injury. J Clin Investig 121(6):2278–2289. doi:10.1172/jci46322
De Palma M, Venneri MA, Galli R, Sergi Sergi L, Politi LS, Sampaolesi M, Naldini L (2005) Tie2 identifies a hematopoietic lineage of proangiogenic monocytes required for tumor vessel formation and a mesenchymal population of pericyte progenitors. Cancer Cell 8(3):211–226. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.08.002
De Palma M, Venneri MA, Roca C, Naldini L (2003) Targeting exogenous genes to tumor angiogenesis by transplantation of genetically modified hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med 9(6):789–795. doi:10.1038/nm871
Takakura N, Huang XL, Naruse T, Hamaguchi I, Dumont DJ, Yancopoulos GD, Suda T (1998) Critical role of the TIE2 endothelial cell receptor in the development of definitive hematopoiesis. Immunity 9(5):677–686
Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, Kalb RG, O’Connor DS, Li F, Altieri DC, Sessa WC (2000) Angiopoietin-1 inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis via the Akt/survivin pathway. J Biol Chem 275(13):9102–9105
DeBusk LM, Hallahan DE, Lin PC (2004) Akt is a major angiogenic mediator downstream of the Ang1/Tie2 signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 298(1):167–177. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.04.013
Dallabrida SM, Ismail N, Oberle JR, Himes BE, Rupnick MA (2005) Angiopoietin-1 promotes cardiac and skeletal myocyte survival through integrins. Circ Res 96(4):e8–e24. doi:10.1161/01.res.0000158285.57191.60
Gavard J, Patel V, Gutkind JS (2008) Angiopoietin-1 prevents VEGF-induced endothelial permeability by sequestering Src through mDia. Dev Cell 14(1):25–36. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2007.10.019
Hughes DP, Marron MB, Brindle NP (2003) The antiinflammatory endothelial tyrosine kinase Tie2 interacts with a novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor ABIN-2. Circ Res 92(6):630–636. doi:10.1161/01.res.0000063422.38690.dc
Jeon BH, Khanday F, Deshpande S, Haile A, Ozaki M, Irani K (2003) Tie-ing the antiinflammatory effect of angiopoietin-1 to inhibition of NF-kappaB. Circ Res 92(6):586–588. doi:10.1161/01.res.0000066881.04116.45
Kim I, Moon SO, Park SK, Chae SW, Koh GY (2001) Angiopoietin-1 reduces VEGF-stimulated leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells by reducing ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin expression. Circ Res 89(6):477–479
Gamble JR, Drew J, Trezise L, Underwood A, Parsons M, Kasminkas L, Rudge J, Yancopoulos G, Vadas MA (2000) Angiopoietin-1 is an antipermeability and anti-inflammatory agent in vitro and targets cell junctions. Circ Res 87(7):603–607
Kim I, Ryu YS, Kwak HJ, Ahn SY, Oh JL, Yancopoulos GD, Gale NW, Koh GY (2002) EphB ligand, ephrinB2, suppresses the VEGF- and angiopoietin 1-induced Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in venous endothelial cells. FASEB J 16(9):1126–1128. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0805fje
Augustin HG, Koh GY, Thurston G, Alitalo K (2009) Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(3):165–177. doi:10.1038/nrm2639
Kobayashi H, DeBusk LM, Babichev YO, Dumont DJ, Lin PC (2006) Hepatocyte growth factor mediates angiopoietin-induced smooth muscle cell recruitment. Blood 108(4):1260–1266. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-09-012807
Cho CH, Kim KE, Byun J, Jang HS, Kim DK, Baluk P, Baffert F, Lee GM, Mochizuki N, Kim J, Jeon BH, McDonald DM, Koh GY (2005) Long-term and sustained COMP-Ang1 induces long-lasting vascular enlargement and enhanced blood flow. Circ Res 97(1):86–94. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000174093.64855.a6
Chae JK, Kim I, Lim ST, Chung MJ, Kim WH, Kim HG, Ko JK, Koh GY (2000) Coadministration of angiopoietin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor enhances collateral vascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(12):2573–2578
Uemura A, Ogawa M, Hirashima M, Fujiwara T, Koyama S, Takagi H, Honda Y, Wiegand SJ, Yancopoulos GD, Nishikawa S (2002) Recombinant angiopoietin-1 restores higher-order architecture of growing blood vessels in mice in the absence of mural cells. J Clin Investig 110(11):1619–1628. doi:10.1172/jci15621
Thurston G, Rudge JS, Ioffe E, Zhou H, Ross L, Croll SD, Glazer N, Holash J, McDonald DM, Yancopoulos GD (2000) Angiopoietin-1 protects the adult vasculature against plasma leakage. Nat Med 6(4):460–463. doi:10.1038/74725
Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Zhou H, Oldmixon EH, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1998) Increased vascularization in mice overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 282(5388):468–471
Smith AH, Kuliszewski MA, Liao C, Rudenko D, Stewart DJ, Leong-Poi H (2012) Sustained improvement in perfusion and flow reserve after temporally separated delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Am Coll Cardiol 59(14):1320–1328. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.12.025
Zhou L, Ma W, Yang Z, Zhang F, Lu L, Ding Z, Ding B, Ha T, Gao X, Li C (2005) VEGF165 and angiopoietin-1 decreased myocardium infarct size through phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Bcl-2 pathways. Gene Ther 12(3):196–202. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302416
Samuel SM, Akita Y, Paul D, Thirunavukkarasu M, Zhan L, Sudhakaran PR, Li C, Maulik N (2010) Coadministration of adenoviral vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 enhances vascularization and reduces ventricular remodeling in the infarcted myocardium of type 1 diabetic rats. Diabetes 59(1):51–60. doi:10.2337/db09-0336
Shin HY, Lee YJ, Kim HJ, Park CK, Kim JH, Wang KC, Kim DG, Koh GY, Paek SH (2010) Protective role of COMP-Ang1 in ischemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res 88(5):1052–1063. doi:10.1002/jnr.22274
Park BH, Jang KY, Kim KH, Song KH, Lee SY, Yoon SJ, Kwon KS, Yoo WH, Koh YJ, Yoon KH, Son HH, Koh GY, Kim JR (2009) COMP-Angiopoietin-1 ameliorates surgery-induced ischemic necrosis of the femoral head in rats. Bone 44(5):886–892. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2009.01.366
Jin HR, Kim WJ, Song JS, Piao S, Choi MJ, Tumurbaatar M, Shin SH, Yin GN, Koh GY, Ryu JK, Suh JK (2011) Intracavernous delivery of a designed angiopoietin-1 variant rescues erectile function by enhancing endothelial regeneration in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse. Diabetes 60(3):969–980. doi:10.2337/db10-0354
Jung YJ, Kim DH, Lee AS, Lee S, Kang KP, Lee SY, Jang KY, Sung MJ, Park SK, Kim W (2009) Peritubular capillary preservation with COMP-angiopoietin-1 decreases ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(4):F952–F960. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00064.2009
Holopainen T, Huang H, Chen C, Kim KE, Zhang L, Zhou F, Han W, Li C, Yu J, Wu J, Koh GY, Alitalo K, He Y (2009) Angiopoietin-1 overexpression modulates vascular endothelium to facilitate tumor cell dissemination and metastasis establishment. Cancer Res 69(11):4656–4664. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-4654
Sullivan CC, Du L, Chu D, Cho AJ, Kido M, Wolf PL, Jamieson SW, Thistlethwaite PA (2003) Induction of pulmonary hypertension by an angiopoietin 1/TIE2/serotonin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(21):12331–12336. doi:10.1073/pnas.1933740100
Taura K, De Minicis S, Seki E, Hatano E, Iwaisako K, Osterreicher CH, Kodama Y, Miura K, Ikai I, Uemoto S, Brenner DA (2008) Hepatic stellate cells secrete angiopoietin 1 that induces angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135(5):1729–1738. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.065
Felcht M, Luck R, Schering A, Seidel P, Srivastava K, Hu J, Bartol A, Kienast Y, Vettel C, Loos EK, Kutschera S, Bartels S, Appak S, Besemfelder E, Terhardt D, Chavakis E, Wieland T, Klein C, Thomas M, Uemura A, Goerdt S, Augustin HG (2012) Angiopoietin-2 differentially regulates angiogenesis through TIE2 and integrin signaling. J Clin Investig 122(6):1991–2005. doi:10.1172/jci58832
Anisimov A, Tvorogov D, Alitalo A, Leppanen VM, An Y, Han EC, Orsenigo F, Gaal EI, Holopainen T, Koh YJ, Tammela T, Korpisalo P, Keskitalo S, Jeltsch M, Yla-Herttuala S, Dejana E, Koh GY, Choi C, Saharinen P, Alitalo K (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factor-angiopoietin chimera with improved properties for therapeutic angiogenesis. Circulation 127(4):424–434. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.112.127472
Gale NW, Thurston G, Hackett SF, Renard R, Wang Q, McClain J, Martin C, Witte C, Witte MH, Jackson D, Suri C, Campochiaro PA, Wiegand SJ, Yancopoulos GD (2002) Angiopoietin-2 is required for postnatal angiogenesis and lymphatic patterning, and only the latter role is rescued by Angiopoietin-1. Dev Cell 3(3):411–423
Oh H, Takagi H, Suzuma K, Otani A, Matsumura M, Honda Y (1999) Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor selectively up-regulate angiopoietin-2 in bovine microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274(22):15732–15739
Reiss Y, Droste J, Heil M, Tribulova S, Schmidt MH, Schaper W, Dumont DJ, Plate KH (2007) Angiopoietin-2 impairs revascularization after limb ischemia. Circ Res 101(1):88–96. doi:10.1161/circresaha.106.143594
Fiedler U, Scharpfenecker M, Koidl S, Hegen A, Grunow V, Schmidt JM, Kriz W, Thurston G, Augustin HG (2004) The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 is stored in and rapidly released upon stimulation from endothelial cell Weibel-Palade bodies. Blood 103(11):4150–4156. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-10-3685
Scharpfenecker M, Fiedler U, Reiss Y, Augustin HG (2005) The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 destabilizes quiescent endothelium through an internal autocrine loop mechanism. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 4):771–780. doi:10.1242/jcs.01653
Hammes HP, Lin J, Wagner P, Feng Y, Vom Hagen F, Krzizok T, Renner O, Breier G, Brownlee M, Deutsch U (2004) Angiopoietin-2 causes pericyte dropout in the normal retina: evidence for involvement in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 53(4):1104–1110
Plate KH, Scholz A, Dumont DJ (2012) Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapy in malignant gliomas revisited. Acta Neuropathol 124(6):763–775. doi:10.1007/s00401-012-1066-5
Mazzieri R, Pucci F, Moi D, Zonari E, Ranghetti A, Berti A, Politi LS, Gentner B, Brown JL, Naldini L, De Palma M (2011) Targeting the ANG2/TIE2 axis inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by impairing angiogenesis and disabling rebounds of proangiogenic myeloid cells. Cancer Cell 19(4):512–526. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.005
Koutroubakis IE, Xidakis C, Karmiris K, Sfiridaki A, Kandidaki E, Kouroumalis EA (2006) Potential role of soluble angiopoietin-2 and Tie-2 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Clin Invest 36(2):127–132. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01602.x
Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z, Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL, Zhang X, Matthay MA, Ware LB, Homer RJ, Lee PJ, Geick A, de Fougerolles AR, Elias JA (2006) Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death. Nat Med 12(11):1286–1293. doi:10.1038/nm1494
Fiedler U, Reiss Y, Scharpfenecker M, Grunow V, Koidl S, Thurston G, Gale NW, Witzenrath M, Rosseau S, Suttorp N, Sobke A, Herrmann M, Preissner KT, Vajkoczy P, Augustin HG (2006) Angiopoietin-2 sensitizes endothelial cells to TNF-alpha and has a crucial role in the induction of inflammation. Nat Med 12(2):235–239. doi:10.1038/nm1351
Venneri MA, De Palma M, Ponzoni M, Pucci F, Scielzo C, Zonari E, Mazzieri R, Doglioni C, Naldini L (2007) Identification of proangiogenic TIE2-expressing monocytes (TEMs) in human peripheral blood and cancer. Blood 109(12):5276–5285. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-10-053504
Oshima Y, Oshima S, Nambu H, Kachi S, Takahashi K, Umeda N, Shen J, Dong A, Apte RS, Duh E, Hackett SF, Okoye G, Ishibashi K, Handa J, Melia M, Wiegand S, Yancopoulos G, Zack DJ, Campochiaro PA (2005) Different effects of angiopoietin-2 in different vascular beds: new vessels are most sensitive. FASEB J 19(8):963–965. doi:10.1096/fj.04-2209fje
Brownlee M (2005) The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54(6):1615–1625
Liu TS, Pei YH, Peng YP, Chen J, Jiang SS, Gong JB (2014) Oscillating high glucose enhances oxidative stress and apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells. J Endocrinol Invest 37(7):645–651. doi:10.1007/s40618-014-0086-5
Lieb W, Zachariah JP, Xanthakis V, Safa R, Chen MH, Sullivan LM, Larson MG, Smith HM, Yang Q, Mitchell GF, Vita JA, Sawyer DB, Vasan RS (2010) Clinical and genetic correlates of circulating angiopoietin-2 and soluble Tie-2 in the community. Circu Cardiovasc Genet 3(3):300–306. doi:10.1161/circgenetics.109.914556
Lim HS, Lip GY, Blann AD (2005) Angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 in diabetes mellitus: relationship to VEGF, glycaemic control, endothelial damage/dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 180(1):113–118. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.11.004
Rasul S, Reiter MH, Ilhan A, Lampichler K, Wagner L, Kautzky-Willer A (2011) Circulating angiopoietin-2 and soluble Tie-2 in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:55. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-10-55
Singh H, Brindle NP, Zammit VA (2010) High glucose and elevated fatty acids suppress signaling by the endothelium protective ligand angiopoietin-1. Microvasc Res 79(2):121–127. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2010.01.005
Brissova M, Shostak A, Shiota M, Wiebe PO, Poffenberger G, Kantz J, Chen Z, Carr C, Jerome WG, Chen J, Baldwin HS, Nicholson W, Bader DM, Jetton T, Gannon M, Powers AC (2006) Pancreatic islet production of vascular endothelial growth factor—a is essential for islet vascularization, revascularization, and function. Diabetes 55(11):2974–2985. doi:10.2337/db06-0690
Tuo QH, Xiong GZ, Zeng H, Yu HD, Sun SW, Ling HY, Zhu BY, Liao DF, Chen JX (2011) Angiopoietin-1 protects myocardial endothelial cell function blunted by angiopoietin-2 and high glucose condition. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32(1):45–51. doi:10.1038/aps.2010.183
Kampfer H, Pfeilschifter J, Frank S (2001) Expressional regulation of angiopoietin-1 and -2 and the tie-1 and -2 receptor tyrosine kinases during cutaneous wound healing: a comparative study of normal and impaired repair. Lab Invest J Tech Methods Pathol 81(3):361–373
Qiao L, Lu SL, Dong JY, Song F (2011) Abnormal regulation of neo-vascularisation in deep partial thickness scalds in rats with diabetes mellitus. Burns J Int Soc Burn Inj 37(6):1015–1022. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2011.03.020
Watanabe D, Suzuma K, Suzuma I, Ohashi H, Ojima T, Kurimoto M, Murakami T, Kimura T, Takagi H (2005) Vitreous levels of angiopoietin 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 139(3):476–481. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2004.10.004
Chong AY, Caine GJ, Freestone B, Blann AD, Lip GY (2004) Plasma angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and angiopoietin receptor tie-2 levels in congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 43(3):423–428. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.08.042
Anuradha S, Mohan V, Gokulakrishnan K, Dixit M (2010) Angiopoietin-2 levels in glucose intolerance, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome in Asian Indians (Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study-74). Metab Clin Exp 59(6):774–779. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2009.09.022
Li L, Qian L, Yu ZQ (2015) Serum angiopoietin-2 is associated with angiopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complicat 29(4):568–571. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.02.006
Li L, Yu ZQ, Qian L, Xu JY, Liu F, Zhao GC, Zhang L, Gu HM, Zhang SJ, Meng J (2016) Interleukin-19 and angiopoietin-2 can enhance angiogenesis of diabetic complications. J Diabetes Complicat 30(2):386–387. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.11.002
Li L, ZHeng-Qing Y, Juan-Yu H, Jian-Yong X, Fan L, Guang-Chun Z, Lei Z, Hui-Ming G, Si-Jing Z, Meng J (2016) Association between interleukin-19 and angiopoietin-2 with vascular complications in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Invest 21. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12519
Luo C, Li T, Zhang C, Chen Q, Li Z, Liu J, Wang Y (2014) Therapeutic effect of alprostadil in diabetic nephropathy: possible roles of angiopoietin-2 and IL-18. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 34(3):916–928. doi:10.1159/000366309
Lee S, Kim W, Moon SO, Sung MJ, Kim DH, Kang KP, Jang KY, Lee SY, Park BH, Koh GY, Park SK (2007) Renoprotective effect of COMP-angiopoietin-1 in db/db mice with type 2 diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transpl 22(2):396–408. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl598
Kosacka J, Nowicki M, Kloting N, Kern M, Stumvoll M, Bechmann I, Serke H, Bluher M (2012) COMP-angiopoietin-1 recovers molecular biomarkers of neuropathy and improves vascularisation in sciatic nerve of ob/ob mice. PLoS One 7(3):e32881. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032881
Sung HK, Kim YW, Choi SJ, Kim JY, Jeune KH, Won KC, Kim JK, Koh GY, Park SY (2009) COMP-angiopoietin-1 enhances skeletal muscle blood flow and insulin sensitivity in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(2):E402–E409. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00122.2009
Chang FC, Lai TS, Chiang CK, Chen YM, Wu MS, Chu TS, Wu KD, Lin SL (2013) Angiopoietin-2 is associated with albuminuria and microinflammation in chronic kidney disease. PLoS One 8(3):e54668. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054668
Chen S, Li H, Zhang C, Li Z, Wang Q, Guo J, Luo C, Wang Y (2015) Urinary angiopoietin-2 is associated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol 2015:163120. doi:10.1155/2015/163120
He FF, Li HQ, Huang QX, Wang QY, Jiang HJ, Chen S, Su H, Zhang C, Wang YM (2015) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine are associated with elevated urinary angiopoietin-2 level in type 2 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Kidney Blood Press Res 40(4):355–365. doi:10.1159/000368510
Khairoun M, van den Heuvel M, van den Berg BM, Sorop O, de Boer R, van Ditzhuijzen NS, Bajema IM, Baelde HJ, Zandbergen M, Duncker DJ, Rabelink TJ, Reinders ME, van der Giessen WJ, Rotmans JI (2015) Early systemic microvascular damage in pigs with atherogenic diabetes mellitus coincides with renal angiopoietin dysbalance. PLoS One 10(4):e0121555. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0121555
Tryggvason K, Patrakka J, Wartiovaara J (2006) Hereditary proteinuria syndromes and mechanisms of proteinuria. New Engl J Med 354(13):1387–1401. doi:10.1056/NEJMra052131
Davis B, Dei Cas A, Long DA, White KE, Hayward A, Ku CH, Woolf AS, Bilous R, Viberti G, Gnudi L (2007) Podocyte-specific expression of angiopoietin-2 causes proteinuria and apoptosis of glomerular endothelia. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 18(8):2320–2329. doi:10.1681/asn.2006101093
Lee KS, Lee KY, Kim SR, Park HS, Park SJ, Min KH, Cho CH, Koh GY, Lee YC (2007) Blockade of airway inflammation and hyper-responsiveness by an angiopoietin-1 variant, COMP-Ang1. Exp Mol Med 39(6):733–745. doi:10.1038/emm.2007.80
Dessapt-Baradez C, Woolf AS, White KE, Pan J, Huang JL, Hayward AA, Price KL, Kolatsi-Joannou M, Locatelli M, Diennet M, Webster Z, Smillie SJ, Nair V, Kretzler M, Cohen CD, Long DA, Gnudi L (2014) Targeted glomerular angiopoietin-1 therapy for early diabetic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 25(1):33–42. doi:10.1681/asn.2012121218
Frank RN (2004) Diabetic retinopathy. New Engl J Med 350(1):48–58. doi:10.1056/NEJMra021678
Rangasamy S, Srinivasan R, Maestas J, McGuire PG, Das A (2011) A potential role for angiopoietin 2 in the regulation of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(6):3784–3791. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-6386
Loukovaara S, Robciuc A, Holopainen JM, Lehti K, Pessi T, Liinamaa J, Kukkonen KT, Jauhiainen M, Koli K, Keski-Oja J, Immonen I (2013) Ang-2 upregulation correlates with increased levels of MMP-9, VEGF, EPO and TGFbeta1 in diabetic eyes undergoing vitrectomy. Acta Ophthalmol 91(6):531–539. doi:10.1111/j.1755-3768.2012.02473.x
Pfister F, Wang Y, Schreiter K, vom Hagen F, Altvater K, Hoffmann S, Deutsch U, Hammes HP, Feng Y (2010) Retinal overexpression of angiopoietin-2 mimics diabetic retinopathy and enhances vascular damages in hyperglycemia. Acta Diabetol 47(1):59–64. doi:10.1007/s00592-009-0099-2
Feng Y, vom Hagen F, Pfister F, Djokic S, Hoffmann S, Back W, Wagner P, Lin J, Deutsch U, Hammes HP (2007) Impaired pericyte recruitment and abnormal retinal angiogenesis as a result of angiopoietin-2 overexpression. Thromb Haemost 97(1):99–108
Cahoon JM, Rai RR, Carroll LS, Uehara H, Zhang X, O’Neil CL, Medina RJ, Das SK, Muddana SK, Olson PR, Nielson S, Walker K, Flood MM, Messenger WB, Archer BJ, Barabas P, Krizaj D, Gibson CC, Li DY, Koh GY, Gao G, Stitt AW, Ambati BK (2015) Intravitreal AAV2.COMP-ang1 prevents neurovascular degeneration in a murine model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 64(12):4247–4259. doi:10.2337/db14-1030
Iribarren C, Phelps BH, Darbinian JA, McCluskey ER, Quesenberry CP, Hytopoulos E, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N (2011) Circulating angiopoietins-1 and -2, angiopoietin receptor Tie-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor-A as biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction: a prospective nested case-control study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 11:31. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-11-31
Chen JX, Stinnett A (2008) Disruption of Ang-1/Tie-2 signaling contributes to the impaired myocardial vascular maturation and angiogenesis in type II diabetic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(9):1606–1613. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.108.169235
Chen JX, Stinnett A (2008) Ang-1 gene therapy inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha)-prolyl-4-hydroxylase-2, stabilizes HIF-1alpha expression, and normalizes immature vasculature in db/db mice. Diabetes 57(12):3335–3343. doi:10.2337/db08-0503
Gonzalez-Quesada C, Cavalera M, Biernacka A, Kong P, Lee DW, Saxena A, Frunza O, Dobaczewski M, Shinde A, Frangogiannis NG (2013) Thrombospondin-1 induction in the diabetic myocardium stabilizes the cardiac matrix in addition to promoting vascular rarefaction through angiopoietin-2 upregulation. Circ Res 113(12):1331–1344. doi:10.1161/circresaha.113.302593
Su H, Takagawa J, Huang Y, Arakawa-Hoyt J, Pons J, Grossman W, Kan YW (2009) Additive effect of AAV-mediated angiopoietin-1 and VEGF expression on the therapy of infarcted heart. Int J Cardiol 133(2):191–197. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.12.034
Takahashi K, Ito Y, Morikawa M, Kobune M, Huang J, Tsukamoto M, Sasaki K, Nakamura K, Dehari H, Ikeda K, Uchida H, Hirai S, Abe T, Hamada H (2003) Adenoviral-delivered angiopoietin-1 reduces the infarction and attenuates the progression of cardiac dysfunction in the rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Ther 8(4):584–592
Chen JX, Zeng H, Reese J, Aschner JL, Meyrick B (2012) Overexpression of angiopoietin-2 impairs myocardial angiogenesis and exacerbates cardiac fibrosis in the diabetic db/db mouse model. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302(4):H1003–H1012. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00866.2011
Liu X, Chen Y, Zhang F, Chen L, Ha T, Gao X, Li C (2007) Synergistically therapeutic effects of VEGF165 and angiopoietin-1 on ischemic rat myocardium. Scand Cardiovasc J SCJ 41(2):95–101. doi:10.1080/14017430701197593
Siddiqui AJ, Blomberg P, Wardell E, Hellgren I, Eskandarpour M, Islam KB, Sylven C (2003) Combination of angiopoietin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy enhances arteriogenesis in the ischemic myocardium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310(3):1002–1009
Golledge J, Clancy P, Maguire J, Lincz L, Koblar S, McEvoy M, Attia J, Levi C, Sturm J, Almeida OP, Yeap BB, Flicker L, Norman PE, Hankey GJ (2014) Plasma angiopoietin-1 is lower after ischemic stroke and associated with major disability but not stroke incidence. Stroke J Cereb Circ 45(4):1064–1068. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.113.004339
Cui X, Chopp M, Zacharek A, Ye X, Roberts C, Chen J (2011) Angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway mediates type 2 diabetes induced vascular damage after cerebral stroke. Neurobiol Dis 43(1):285–292. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.04.005
Corona G, Giorda CB, Cucinotta D, Guida P, Nada E (2013) SUBITO-DE study group. The SUBITO-DE study: sexual dysfunction in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes male patients. J Endocrinol Invest 36(10):864–868. doi:10.3275/8969
Yin GN, Choi MJ, Kim WJ, Kwon MH, Song KM, Park JM, Das ND, Kwon KD, Batbold D, Oh GT, Koh GY, Kim KW, Ryu JK, Suh JK (2014) Inhibition of Ninjurin 1 restores erectile function through dual angiogenic and neurotrophic effects in the diabetic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(26):E2731–E2740. doi:10.1073/pnas.1403471111
Jin HR, Chung YG, Kim WJ, Zhang LW, Piao S, Tuvshintur B, Yin GN, Shin SH, Tumurbaatar M, Han JY, Ryu JK, Suh JK (2010) A mouse model of cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction: functional and morphological characterization of the corpus cavernosum. J Sex Med 7(10):3351–3364. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01942.x
Ryu JK, Kim WJ, Koh YJ, Piao S, Jin HR, Lee SW, Choi MJ, Shin HY, Kwon MH, Jung K, Koh GY, Suh JK (2015) Designed angiopoietin-1 variant, COMP-angiopoietin-1, rescues erectile function through healthy cavernous angiogenesis in a hypercholesterolemic mouse. Sci Rep 5:9222. doi:10.1038/srep09222
Kim SO, Lee HS, Ahn K, Park K (2013) COMP-angiopoietin-1 promotes cavernous angiogenesis in a type 2 diabetic rat model. J Korean Med Sci 28(5):725–730. doi:10.3346/jkms.2013.28.5.725
Cho CH, Sung HK, Kim KT, Cheon HG, Oh GT, Hong HJ, Yoo OJ, Koh GY (2006) COMP-angiopoietin-1 promotes wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and blood flow in a diabetic mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(13):4946–4951. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506352103
Mannucci E, Dicembrini I, Lauria A, Pozzilli P (2013) Is glucose control important for prevention of cardiovascular disease in diabetes? Diabetes Care 36(Suppl 2):S259–S263. doi:10.2337/dcS13-2018
Ferrannini E, DeFronzo RA (2015) Impact of glucose-lowering drugs on cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Eur Heart J 36(34):2288–2296. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv239
Cho CH, Kammerer RA, Lee HJ, Steinmetz MO, Ryu YS, Lee SH, Yasunaga K, Kim KT, Kim I, Choi HH, Kim W, Kim SH, Park SK, Lee GM, Koh GY (2004) COMP-Ang1: a designed angiopoietin-1 variant with nonleaky angiogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(15):5547–5552. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307574101
Kim SR, Lee KS, Park SJ, Min KH, Lee KY, Choe YH, Hong SH, Koh GY, Lee YC (2008) Angiopoietin-1 variant, COMP-Ang1 attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced acute lung injury. Exp Mol Med 40(3):320–331. doi:10.3858/emm.2008.40.3.320
Kim DH, Jung YJ, Lee AS, Lee S, Kang KP, Lee TH, Lee SY, Jang KY, Moon WS, Choi KS, Yoon KH, Sung MJ, Park SK, Kim W (2009) COMP-angiopoietin-1 decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 76(11):1180–1191. doi:10.1038/ki.2009.387
Oh N, Kim K, Kim SJ, Park I, Lee JE, Seo YS, An HJ, Kim HM, Koh GY (2015) A designed angiopoietin-1 variant, dimeric CMP-Ang1 activates Tie2 and stimulates angiogenesis and vascular stabilization in n-glycan dependent manner. Sci Rep 5:15291. doi:10.1038/srep15291
Lambert NG, Zhang X, Rai RR, Uehara H, Choi S, Carroll LS, Das SK, Cahoon JM, Kirk BH, Bentley BM, Ambati BK (2016) Subretinal AAV2.COMP-Ang1 suppresses choroidal neovascularization and vascular endothelial growth factor in a murine model of age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res 145:248–257. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2016.01.009
Paul A, Binsalamah ZM, Khan AA, Abbasia S, Elias CB, Shum-Tim D, Prakash S (2011) A nanobiohybrid complex of recombinant baculovirus and Tat/DNA nanoparticles for delivery of Ang-1 transgene in myocardial infarction therapy. Biomaterials 32(32):8304–8318. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.07.042
Chiu LL, Radisic M (2010) Scaffolds with covalently immobilized VEGF and Angiopoietin-1 for vascularization of engineered tissues. Biomaterials 31(2):226–241. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.039
Saif J, Schwarz TM, Chau DY, Henstock J, Sami P, Leicht SF, Hermann PC, Alcala S, Mulero F, Shakesheff KM, Heeschen C, Aicher A (2010) Combination of injectable multiple growth factor-releasing scaffolds and cell therapy as an advanced modality to enhance tissue neovascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30(10):1897–1904. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.110.207928
Khan AA, Paul A, Abbasi S, Prakash S (2011) Mitotic and antiapoptotic effects of nanoparticles coencapsulating human VEGF and human angiopoietin-1 on vascular endothelial cells. Int J Nanomed 6:1069–1081. doi:10.2147/ijn.s15054
Van Slyke P, Alami J, Martin D, Kuliszewski M, Leong-Poi H, Sefton MV, Dumont D (2009) Acceleration of diabetic wound healing by an angiopoietin peptide mimetic. Tissue Eng Part A 15(6):1269–1280. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2007.0400
Tournaire R, Simon MP, le Noble F, Eichmann A, England P, Pouyssegur J (2004) A short synthetic peptide inhibits signal transduction, migration and angiogenesis mediated by Tie2 receptor. EMBO Rep 5(3):262–267. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400100
Rubig E, Stypmann J, Van Slyke P, Dumont DJ, Spieker T, Buscher K, Reuter S, Goerge T, Pavenstadt H, Kumpers P (2016) The synthetic tie2 agonist peptide vasculotide protects renal vascular barrier function in experimental acute kidney injury. Sci Rep 6:22111. doi:10.1038/srep22111
Brown JL, Cao ZA, Pinzon-Ortiz M, Kendrew J, Reimer C, Wen S, Zhou JQ, Tabrizi M, Emery S, McDermott B, Pablo L, McCoon P, Bedian V, Blakey DC (2010) A human monoclonal anti-ANG2 antibody leads to broad antitumor activity in combination with VEGF inhibitors and chemotherapy agents in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther 9(1):145–156. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-09-0554
Falcon BL, Hashizume H, Koumoutsakos P, Chou J, Bready JV, Coxon A, Oliner JD, McDonald DM (2009) Contrasting actions of selective inhibitors of angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 on the normalization of tumor blood vessels. Am J Pathol 175(5):2159–2170. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.090391
Oliner J, Min H, Leal J, Yu D, Rao S, You E, Tang X, Kim H, Meyer S, Han SJ, Hawkins N, Rosenfeld R, Davy E, Graham K, Jacobsen F, Stevenson S, Ho J, Chen Q, Hartmann T, Michaels M, Kelley M, Li L, Sitney K, Martin F, Sun JR, Zhang N, Lu J, Estrada J, Kumar R, Coxon A, Kaufman S, Pretorius J, Scully S, Cattley R, Payton M, Coats S, Nguyen L, Desilva B, Ndifor A, Hayward I, Radinsky R, Boone T, Kendall R (2004) Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by selective inhibition of angiopoietin-2. Cancer Cell 6(5):507–516. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.030
Huang H, Lai JY, Do J, Liu D, Li L, Del Rosario J, Doppalapudi VR, Pirie-Shepherd S, Levin N, Bradshaw C, Woodnutt G, Lappe R, Bhat A (2011) Specifically targeting angiopoietin-2 inhibits angiogenesis, Tie2-expressing monocyte infiltration, and tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res 17(5):1001–1011. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-2317
Davis ME, Zuckerman JE, Choi CH, Seligson D, Tolcher A, Alabi CA, Yen Y, Heidel JD, Ribas A (2010) Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nature 464(7291):1067–1070. doi:10.1038/nature08956
White RR, Shan S, Rusconi CP, Shetty G, Dewhirst MW, Kontos CD, Sullenger BA (2003) Inhibition of rat corneal angiogenesis by a nuclease-resistant RNA aptamer specific for angiopoietin-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(9):5028–5033. doi:10.1073/pnas.0831159100
Rennel ES, Regula JT, Harper SJ, Thomas M, Klein C, Bates DO (2011) A human neutralizing antibody specific to Ang-2 inhibits ocular angiogenesis. Microcirculation 18(7):598–607. doi:10.1111/j.1549-8719.2011.00120.x
Sanada F, Kanbara Y, Taniyama Y, Otsu R, Carracedo M, Ikeda-Iwabu Y, Muratsu J, Sugimoto K, Yamamoto K, Rakugi H, Morishita R (2016) Induction of angiogenesis by a type III phosphodiesterase inhibitor, cilostazol, through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and cAMP pathways in vascular cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36(3):545–552. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.115.307011
Giannetta E, Feola T, Gianfrilli D, Pofi R, Dall’Armi V, Badagliacca R, Barbagallo F, Lenzi A, Isidori AM (2014) Is chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 5 cardioprotective and safe? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Med 12(1):185. doi:10.1186/s12916-014-0185-3
Giannetta E, Isidori AM, Galea N, Carbone I, Mandosi E, Vizza CD, Naro F, Morano S, Fedele F, Lenzi A (2012) Chronic Inhibition of cGMP phosphodiesterase 5A improves diabetic cardiomyopathy: a randomized, controlled clinical trial using magnetic resonance imaging with myocardial tagging. Circulation 125(19):2323–2333. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.111.063412
Santi D, Giannetta E, Isidori AM, Vitale C, Aversa A, Simoni M (2015) Therapy of endocrine disease. Effects of chronic use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on endothelial markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol/Eur Fed Endocr Soc 172(3):R103–R114. doi:10.1530/eje-14-0700
Di Luigi L, Corinaldesi C, Colletti M, Scolletta S, Antinozzi C, Vannelli GB, Giannetta E, Gianfrilli D, Isidori AM, Migliaccio S, Poerio N, Fraziano M, Lenzi A, Crescioli C (2016) Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor sildenafil decreases the proinflammatory chemokine CXCL10 in human cardiomyocytes and in subjects with diabetic cardiomyopathy. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-016-0359-6
Fiore D, Gianfrilli D, Giannetta E, Galea N, Panio G, di Dato C, Pofi R, Pozza C, Sbardella E, Carbone I, Naro F, Lenzi A, Venneri MA, Isidori AM (2016) PDE5 inhibition ameliorates visceral adiposity targeting the miR-22/SIRT1 pathway: evidence from the CECSID trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(4):1525–1534. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-4252
Mandosi E, Giannetta E, Filardi T, Lococo M, Bertolini C, Fallarino M, Gianfrilli D, Venneri MA, Lenti L, Lenzi A, Morano S (2015) Endothelial dysfunction markers as a therapeutic target for Sildenafil treatment and effects on metabolic control in type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Ther Targ 19(12):1617–1622. doi:10.1517/14728222.2015.1066337
Venneri MA, Giannetta E, Panio G, De Gaetano R, Gianfrilli D, Pofi R, Masciarelli S, Fazi F, Pellegrini M, Lenzi A, Naro F, Isidori AM (2015) Chronic inhibition of PDE5 limits pro-inflammatory monocyte-macrophage polarization in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. PLoS One 10(5):e0126580. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126580
Pofi R, Gianfrilli D, Badagliacca R, Di Dato C, Venneri MA, Giannetta E (2016) Everything you ever wanted to know about phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and the heart (but never dared ask): How do they work? J Endocrinol Invest 39(2):131–142. doi:10.1007/s40618-015-0339-y
Corinaldesi C, Di Luigi L, Lenzi A, Crescioli C (2016) Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: back and forward from cardiac indications. J Endocrinol Invest 39(2):143–151. doi:10.1007/s40618-015-0340-5
Wang L, Chopp M, Szalad A, Jia L, Lu X, Lu M, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zhang ZG (2015) Sildenafil ameliorates long term peripheral neuropathy in type II diabetic mice. PLoS One 10(2):e0118134. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118134
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marie-Hélène Hayles for revision of the English text.
Funding
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Instruction, University and Research (MIUR) Grant FIRB Futuro in Ricerca RBFR10URHP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. M. I. has been an occasional consultant for Otsuka, Shire, Novartis, and Menarini. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
This review has been commissioned to Andrea M. Isidori winner of the Italian Society of Endocrinology “Under 40 SIE award” for the year 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isidori, A.M., Venneri, M.A. & Fiore, D. Angiopoietin-1 and Angiopoietin-2 in metabolic disorders: therapeutic strategies to restore the highs and lows of angiogenesis in diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 1235–1246 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0502-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0502-0