Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of sitagliptin 100 mg/day in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes.
Design
A post hoc pooled analysis of 25 randomized, double-blind, parallel group clinical studies with results available as of 1 December 2011.
Setting
Multicenter, international clinical trials.
Subjects
Patients with type 2 diabetes aged 65 years or older.
Interventions
Patients were randomized to sitagliptin 100 mg/day (n = 1,261) or a comparator (n = 1,185) for 12 weeks to 2 years.
Main Outcome Measures
In each study, investigators reported serious and non-serious adverse events that occurred during the study, and serious adverse events occurring within 14 days following the last dose of study drug. This analysis used patient-level data from each study to assess the exposure-adjusted incidence rates of specific adverse events that occurred following initiation of study drug.
Results
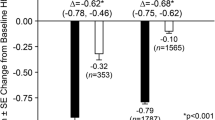
Summary measures of adverse events overall were similar between the sitagliptin and non-exposed (active comparator or placebo) groups, except for higher incidences of deaths and drug-related adverse events in the non-exposed group. Incidence rates of specific adverse events were generally similar between the two groups, with the exception of hypoglycemia. A lower incidence rate of hypoglycemia was observed in the sitagliptin group compared with the non-exposed group [7.0 vs. 14.3 per 100 patient-years; difference −7.6 (95 % CI −11.2 to −4.3]), primarily due to greater use of sulfonylureas in the non-exposed group.
Conclusions
In this pooled safety analysis of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes, treatment with sitagliptin 100 mg/day was generally well tolerated for up to 2 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sloan FA, Bethel MA, Ruiz D Jr, Shea AM, Feinglos MN. The growing burden of diabetes mellitus in the US elderly population. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(2):192–9.
Cowie CC, Rust KF, Ford ES, Eberhardt MS, Byrd-Holt DD, Li C, et al. Full accounting of diabetes and pre-diabetes in the U.S. population in 1988–1994 and 2005–2006. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(2):287–94.
Kirkman MS, Briscoe VJ, Clark N, Florez H, Haas LB, Halter JB, et al. Diabetes in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(12):2650–64.
Trends in aging: United States and worldwide. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2003;52:101–4,106.
Bertoni AG, Hundley WG, Massing MW, Bonds DE, Burke GL, Goff DC Jr. Heart failure prevalence, incidence, and mortality in the elderly with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(3):699–703.
Bethel MA, Sloan FA, Belsky D, Feinglos MN. Longitudinal incidence and prevalence of adverse outcomes of diabetes mellitus in elderly patients. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(9):921–7.
Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(4):229–34.
Brown AF, Mangione CM, Saliba D, Sarkisian CA. Guidelines for improving the care of the older person with diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(5 Suppl Guidelines):S265–80.
Chen LK, Chen YM, Lin MH, Peng LN, Hwang SJ. Care of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus: a focus on frailty. Ageing Res Rev. 2010;9(Suppl 1):S18–22.
Kalyani RR, Saudek CD, Brancati FL, Selvin E. Association of diabetes, comorbidities, and A1C with functional disability in older adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1999–2006. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(5):1055–60.
Soe K, Sacerdote A, Karam J, Bahtiyar G. Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Maturitas. 2011;70(2):151–9.
Inzucchi SE. Oral antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes: scientific review. JAMA. 2002;287(3):360–72.
Sinclair AJ, Alexander CM, Davies MJ, Zhao C, Mavros P. Factors associated with initiation of antihyperglycaemic medication in UK patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. BMC Endocr Disord. 2012;12:1.
Zhang Q, Rajagopalan S, Marrett E, Davies MJ, Radican L, Engel SS. Time to treatment initiation with oral antihyperglycaemic therapy in US patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(2):149–54.
Zammitt NN, Frier BM. Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes: pathophysiology, frequency, and effects of different treatment modalities. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(12):2948–61.
Yki-Jarvinen H. Thiazolidinediones. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(11):1106–18.
Cariou B, Charbonnel B, Staels B. Thiazolidinediones and PPARgamma agonists: time for a reassessment. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012;23(5):205–15.
Deacon CF, Mannucci E, Ahren B. Glycaemic efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors as add-on therapy to metformin in subjects with type 2 diabetes: a review and meta analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(8):762–7.
Pratley RE, Nauck M, Bailey T, Montanya E, Cuddihy R, Filetti S, et al. Liraglutide versus sitagliptin for patients with type 2 diabetes who did not have adequate glycaemic control with metformin: a 26-week, randomised, parallel-group, open-label trial. Lancet. 2010;375(9724):1447–56.
Bergenstal RM, Wysham C, MacConell L, Malloy J, Walsh B, Yan P, et al. Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus sitagliptin or pioglitazone as an adjunct to metformin for treatment of type 2 diabetes (DURATION-2): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9739):431–9.
Engel SS, Round E, Golm GT, Kaufman KD, Goldstein BJ. Safety and tolerability of sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes: pooled analysis of 25 clinical studies. Diabetes Ther. 2013;4(1):119–45.
Barzilai N, Guo H, Mahoney EM, Caporossi S, Golm GT, Langdon RB, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of sitagliptin monotherapy in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27(5):1049–58.
Miettinen O, Nurminen M. Comparative analysis of two rates. Stat Med. 1985;4(2):213–26.
Pratley RE, Rosenstock J, Pi-Sunyer FX, Banerji MA, Schweizer A, Couturier A, Dejager S. Management of type 2 diabetes in treatment-naive elderly patients: benefits and risks of vildagliptin monotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(12):3017–22.
Pratley RE, McCall T, Fleck PR, Wilson CA, Mekki Q. Alogliptin use in elderly people: a pooled analysis from phase 2 and 3 studies. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57(11):2011–9.
Bramlage P, Gitt AK, Binz C, Krekler M, Deeg E, Tschope D. Oral antidiabetic treatment in type-2 diabetes in the elderly: balancing the need for glucose control and the risk of hypoglycemia. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012;11:122.
Ligthelm RJ, Kaiser M, Vora J, Yale JF. Insulin use in elderly adults: risk of hypoglycemia and strategies for care. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(8):1564–70.
Hermansen K, Kipnes M, Luo E, Fanurik D, Khatami H, Stein P. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on glimepiride alone or on glimepiride and metformin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007;9(5):733–45.
Vilsboll T, Rosenstock J, Yki-Jarvinen H, Cefalu WT, Chen Y, Luo E, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12(2):167–77.
Shyangdan DS, Royle P, Clar C, Sharma P, Waugh N, Snaith A. Glucagon-like peptide analogues for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;(10):CD006423.
Aschner P, Katzeff H, Guo H, Sunga S, Williams-Herman D, Kaufman KD, Goldstein BJ. Efficacy and safety of monotherapy of sitagliptin compared with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12(3):252–61.
Iwamoto Y, Tajima N, Kadowaki T, Nonaka K, Taniguchi T, Nishii M, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin monotherapy compared with voglibose in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12(7):613–22.
Goossen K, Graber S. Longer term safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(12):1061–72.
Amori RE, Lau J, Pittas AG. Efficacy and safety of incretin therapy in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2007;298(2):194–206.
Richter B, Bandeira-Echtler E, Bergerhoff K, Lerch CL. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008;(2):CD006739.
Bethel MA, Green J, Califf RM, Holman RR. Rationale and design of the Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS). Diabetologia. 2009;52(Suppl 1):S480.
Scott R, Wu M, Sanchez M, Stein P. Efficacy and tolerability of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy over 12 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2007;61(1):171–80.
Hanefeld M, Herman GA, Wu M, Mickel C, Sanchez M, Stein PP. Once-daily sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23(6):1329–39.
Rosenstock J, Brazg R, Andryuk PJ, Lu K, Stein P. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing pioglitazone therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2006;28(10):1556–68.
Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, Wu M, Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(12):2638–43.
Aschner P, Kipnes MS, Lunceford JK, Sanchez M, Mickel C, Williams-Herman DE. Effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(12):2632–7.
Raz I, Hanefeld M, Xu L, Caria C, Williams-Herman D, Khatami H. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2006;49(11):2564–71.
Seck T, Nauck M, Sheng D, Sunga S, Davies MJ, Stein PP, et al. Safety and efficacy of treatment with sitagliptin or glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 2-year study. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64(5):562–76.
Nauck MA, Meininger G, Sheng D, Terranella L, Stein PP. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, compared with the sulfonylurea, glipizide, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007;9(2):194–205.
Williams-Herman D, Johnson J, Teng R, Luo E, Davies MJ, Kaufman KD, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 54-week study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25(3):569–83.
Williams-Herman D, Johnson J, Teng R, Golm G, Kaufman KD, Goldstein BJ, Amatruda JM. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and metformin as initial combination therapy and as monotherapy over 2 years in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12:442–51.
Goldstein BJ, Feinglos MN, Lunceford JK, Johnson J, Williams-Herman DE. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(8):1979–87.
Mohan V, Yang W, Son HY, Xu L, Noble L, Langdon RB, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes in China, India, and Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009;83(1):106–16.
Dobs AS, Goldstein BJ, Aschner P, Horton ES, Umpierrez GE, Duran L, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin and rosiglitazone combination therapy in a randomized placebo-controlled 54-week trial in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2013;5(1):68–79.
Raz I, Chen Y, Wu M, Hussain S, Kaufman KD, Amatruda JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24(2):537–50.
Alba M, Ahren B, Inzucchi SE, Guan Y, Mallick M, Xu L, et al. Sitagliptin and pioglitazone provide complementary effects on postprandial glucose and pancreatic islet cell function. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(12):1101–10.
Yoon KH, Shockey GR, Teng R, Golm GT, Thakkar PR, Meehan AG, et al. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and pioglitazone on glycemic control and measures of beta-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65(2):154–64.
Yoon KH, Steinberg H, Teng R, Golm GT, Lee M, O’Neill EA, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 54-week study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(8):745–52.
Wainstein J, Katz L, Engel SS, Xu L, Golm GT, Hussain S, et al. Initial therapy with the fixed-dose combination of sitagliptin and metformin results in greater improvement in glycaemic control compared with pioglitazone monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(5):409–18.
Perez-Monteverde A, Seck T, Xu L, Lee MA, Sisk CM, Williams-Herman DE, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and the fixed-dose combination of sitagliptin and metformin vs. pioglitazone in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65(9):930–8.
Yang W, Guan Y, Shentu Y, Li Z, Johnson-Levonas AO, Engel SS, et al. The addition of sitagliptin to ongoing metformin therapy significantly improves glycemic control in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2012;4(3):227–37.
Reasner C, Olansky L, Seck TL, Williams-Herman DE, Chen M, Terranella L, et al. The effect of initial therapy with the fixed-dose combination of sitagliptin and metformin compared with metformin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(7):644–52.
Olansky L, Reasner C, Seck TL, Williams-Herman DE, Chen M, Terranella L, et al. A treatment strategy implementing combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin results in superior glycaemic control versus metformin monotherapy due to a low rate of addition of antihyperglycaemic agents. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(9):841–9.
Henry RR, Staels B, Fonseca VA, Chou MZ, Teng R, Golm GT, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination treatment with sitagliptin and pioglitazone-a factorial study. Diabetes Obes Metab. Epub 2 Aug 2013. doi:10.1111/dom.12194.
Fonseca V, Staels B, Morgan JD, Shentu Y, Golm GT, Johnson-Levonas AO, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin and pioglitazone combination therapy in a randomized, placebo-controlled, 26-week trial in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat. 2013;27(2):177–83.
Scott R, Loeys T, Davies MJ, Engel SS. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10(10):959–69.
Arechavaleta R, Seck T, Chen Y, Krobot KJ, O’Neill EA, Duran L, et al. Efficacy and safety of treatment with sitagliptin or glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(2):160–8.
Acknowledgments
The studies in this pooled analysis were sponsored by Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA.
The authors would like to acknowledge the patients, site investigators and their staffs, and Merck personnel from each study included in this pooled analysis for their participation and efforts. The authors acknowledge the following Merck employees: Helen Wang for her statistical programming efforts, Edward A. O’Neill for editorial assistance, and Jennifer Rotonda for assistance with manuscript submission.
Conflicts of interest
All authors are employed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., the manufacturer of sitagliptin, and may have company stock or stock options.
Author contributions
Elizabeth M. Round, Samuel S. Engel, Gregory T. Golm, Keith D. Kaufman, and Barry J. Goldstein conceived the design for the analyses. Gregory T. Golm performed the statistical analyses. All authors were involved in the interpretation of the analyses, drafting the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and approving the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Round, E.M., Engel, S.S., Golm, G.T. et al. Safety of Sitagliptin in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pooled Analysis of 25 Clinical Studies. Drugs Aging 31, 203–214 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-014-0155-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-014-0155-7