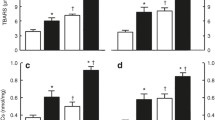
Abstract
Purpose
Presumed interrelationships among deleterious aspects of adipose tissue metabolism, inflammation, and cellular oxidative stress could be influenced by pubertal hormonal changes. They were investigated in pre- and early pubertal normal-weight and obese boys before and after an exercise bout employed as an energy demanding stimulator.
Methods
Cross-sectional study. Seventy-six healthy pre- (mean ± SD, 10.6 ± 0.2 years old, 28 normal-weight, and 11 obese) and early-(11.4 ± 0.2 years old, 25 normal-weight, and 12 obese) pubertal boys, were blood-sampled before and after a bout of exercise at 70% VO2 max. Leptin, adiponectin, markers of inflammation (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, high sensitivity IL-6), pro- (thiobarbitouric acid reactive substances, protein carbonyls) and anti- (glutathione, oxidized glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, catalase, total antioxidant capacity) oxidation were measured.
Results
Baseline and post-exercise adiponectin was greater and leptin and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein were lower in normal-weight than in obese pre- and early pubertal boys, while high sensitivity IL-6 was greater in obese than in normal-weight pre-pubertal boys. In pre-pubertal obese boys: at baseline, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein correlated negatively with catalase; high sensitivity IL-6 correlated positively with protein carbonyls; Δ (difference during exercise) adiponectin correlated positively with Δcatalase. In all boys: at baseline, high sensitivity IL-6 correlated positively with leptin and was the best negative and the second best positive predictor for post-exercise glutathione/oxidized glutathione and protein carbonyls, respectively; leptin was the best negative predictor for post-exercise glutathione; waist to height ratio was the best positive predictor for post-exercise thiobarbitouric acid reactive substances; body mass index z-score and adiponectin were, respectively, the best positive predictor for post-exercise protein carbonyls and catalase.
Conclusions
In all subjects, leptin and adiponectin predict negatively and positively anti-oxidation, respectively, while high sensitivity IL-6 predicts positively and negatively pro- and anti-oxidation, respectively. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is increased and negatively associated with anti-oxidation in pre-pubertal obese boys, suggesting that childhood obesity is associated with aseptic inflammation and oxidative stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Erhardt, R. Foraita, I. Pigeot, G. Barba, T. Veidebaum, M. Tornaritis, N. Michels, G. Eiben, W. Ahrens, L.A. Moreno, E. Kovacs, D. Molnar, Reference values for leptin and adiponectin in children below the age of 10 based on the IDEFICS cohort. Int. J. Obes. (Lond). 38(Suppl 2), S32–38 (2014). doi:10.1038/ijo.2014.133ijo2014133
S.S. Martin, A. Qasim, M.P. Reilly, Leptin resistance: a possible interface of inflammation and metabolism in obesity-related cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 52(15), 1201–1210 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.05.060 S0735-1097(08)02435-2
E. Fuentes, F. Fuentes, G. Vilahur, L. Badimon, I. Palomo, Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 136584 (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/136584
A. Korner, J. Kratzsch, R. Gausche, M. Schaab, S. Erbs, W. Kiess, New predictors of the metabolic syndrome in children-role of adipocytokines. Pediatr. Res. 61(6), 640–645 (2007). doi:10.1203/01.pdr.0000262638.48304.ef
L. Marseglia, S. Manti, G. D’Angelo, A. Nicotera, E. Parisi, G. Di Rosa, E. Gitto, T. Arrigo, Oxidative stress in obesity: a critical component in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16(1), 378–400 (2015). doi:10.3390/ijms16010378ijms16010378
S. Furukawa, T. Fujita, M. Shimabukuro, M. Iwaki, Y. Yamada, Y. Nakajima, O. Nakayama, M. Makishima, M. Matsuda, I. Shimomura, Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 114(12), 1752–1761 (2004). doi:10.1172/JCI21625
A.F. Soares, M. Guichardant, D. Cozzone, N. Bernoud-Hubac, N. Bouzaidi-Tiali, M. Lagarde, A. Geloen, Effects of oxidative stress on adiponectin secretion and lactate production in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 38(7), 882–889 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.12.010
P.W. Franks, R.L. Hanson, W.C. Knowler, M.L. Sievers, P.H. Bennett, H.C. Looker, Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death. N. Engl. J. Med. 362(6), 485–493 (2010). doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0904130
N. Mauras, C. Delgiorno, C. Kollman, K. Bird, M. Morgan, S. Sweeten, P. Balagopal, L. Damaso, Obesity without established comorbidities of the metabolic syndrome is associated with a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state, even before the onset of puberty in children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95(3), 1060–1068 (2010). doi:10.1210/jc.2009-1887jc.2009-1887
A. Nappo, L. Iacoviello, A. Fraterman, E.M. Gonzalez-Gil, C. Hadjigeorgiou, S. Marild, D. Molnar, L.A. Moreno, J. Peplies, I. Sioen, T. Veidebaum, A. Siani, P. Russo, High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is a predictive factor of adiposity in children: results of the identification and prevention of dietary- and lifestyle-induced health effects in children and infants (IDEFICS) study. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2(3), e000101 (2013). doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.0001012/3/e000101
M.L. Hribal, T.V. Fiorentino, G. Sesti, Role of C reactive protein (CRP) in leptin resistance. Curr. Pharm. Des. 20(4), 609–615 (2014). doi:CPD-EPUB-20130514-4
N. Ouchi, S. Kihara, T. Funahashi, T. Nakamura, M. Nishida, M. Kumada, Y. Okamoto, K. Ohashi, H. Nagaretani, K. Kishida, H. Nishizawa, N. Maeda, H. Kobayashi, H. Hiraoka, Y. Matsuzawa, Reciprocal association of C-reactive protein with adiponectin in blood stream and adipose tissue. Circulation. 107(5), 671–674 (2003)
P. Mandal, B.T. Pratt, M. Barnes, M.R. McMullen, L.E. Nagy, Molecular mechanism for adiponectin-dependent M2 macrophage polarization: link between the metabolic and innate immune activity of full-length adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 286(15), 13460–13469 (2011). doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.204644M110.204644
P.J. Simons, P.S. van den Pangaart, J.M. Aerts, L. Boon, Pro-inflammatory delipidizing cytokines reduce adiponectin secretion from human adipocytes without affecting adiponectin oligomerization. J. Endocrinol. 192(2), 289–299 (2007). doi:10.1677/JOE-06-0047
L.E. Hand, P. Usan, G.J. Cooper, L.Y. Xu, B. Ammori, P.S. Cunningham, R. Aghamohammadzadeh, H. Soran, A. Greenstein, A.S. Loudon, D.A. Bechtold, D.W. Ray, Adiponectin induces A20 expression in adipose tissue to confer metabolic benefit. Diabetes. 64(1), 128–136 (2015). doi:10.2337/db13-1835
H. Nascimento, E. Costa, S. Rocha, C. Lucena, P. Rocha-Pereira, C. Rego, H.F. Mansilha, A. Quintanilha, L. Aires, J. Mota, A. Santos-Silva, L. Belo, Adiponectin and markers of metabolic syndrome in obese children and adolescents: impact of 8-mo regular physical exercise program. Pediatr. Res. 76(2), 159–165 (2014). doi:10.1038/pr.2014.73
K. Fisher-Wellman, R.J. Bloomer, Acute exercise and oxidative stress: a 30 year history. Dyn. Med. 8, 1 (2009). doi:10.1186/1476-5918-8-1
G. Paltoglou, I.G. Fatouros, G. Valsamakis, M. Schoina, A. Avloniti, A. Chatzinikolaou, A. Kambas, D. Draganidis, A. Mantzou, M. Papagianni, C. Kanaka-Gantenbein, G.P. Chrousos, G. Mastorakos, Antioxidation improves in puberty in normal weight and obese boys, in positive association with exercise-stimulated growth hormone secretion. Pediatr. Res. 78(2), 158–164 (2015). doi:10.1038/pr.2015.85
R.J. Alleman, L.A. Katunga, M.A. Nelson, D.A. Brown, E.J. Anderson, The “Goldilocks Zone” from a redox perspective-adaptive vs. deleterious responses to oxidative stress in striated muscle. Front Physiol. 5, 358 (2014). doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00358
C.M. Burt Solorzano, C.R. McCartney, Obesity and the pubertal transition in girls and boys. Reproduction 140(3), 399–410 (2010). doi:10.1530/REP-10-0119
J.D. Veldhuis, S.M. Pincus, R. Mitamura, K. Yano, N. Suzuki, Y. Ito, Y. Makita, A. Okuno, Developmentally delimited emergence of more orderly luteinizing hormone and testosterone secretion during late prepuberty in boys. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86(1), 80–89 (2001)
A. Luger, P.A. Deuster, S.B. Kyle, W.T. Gallucci, L.C. Montgomery, P.W. Gold, D.L. Loriaux, G.P. Chrousos, Acute hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to the stress of treadmill exercise. Physiologic adaptations to physical training. N. Engl. J. Med. 316(21), 1309–1315 (1987). doi:10.1056/NEJM198705213162105
G. Mastorakos, M. Pavlatou, Exercise as a stress model and the interplay between the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal and the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axes. Horm. Metab. Res. 37(9), 577–584 (2005). doi:10.1055/s-2005-870426
G. Mastorakos, M. Pavlatou, E. Diamanti-Kandarakis, G.P. Chrousos, Exercise and the stress system. Hormones (Athens) 4(2), 73–89 (2005)
T.J. Cole, M.C. Bellizzi, K.M. Flegal, W.H. Dietz, Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 320(7244), 1240–1243 (2000)
D. Chiotis, X. Krikos, G. Tsiftis, M. Hatzisymeon, M. Maniati-Christidi, A. Dacou-Voutetaki, Body mass index and prevalence of obesity in subjects of Hellenic origin aged 0–18 years living in the Athens area. Ann. Clin. Pediatr. Unive Athen. 51, 139–154 (2004)
K. Albertsson-Wikland, S. Rosberg, B. Lannering, L. Dunkel, G. Selstam, E. Norjavaara, Twenty-four-hour profiles of luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, testosterone, and estradiol levels: a semilongitudinal study throughout puberty in healthy boys. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82(2), 541–549 (1997). doi:10.1210/jcem.82.2.3778
A.S. Kelly, J. Steinberger, T.P. Olson, D.R. Dengel, In the absence of weight loss, exercise training does not improve adipokines or oxidative stress in overweight children. Metabolism 56(7), 1005–1009 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2007.03.009
K. Margonis, I.G. Fatouros, A.Z. Jamurtas, M.G. Nikolaidis, I. Douroudos, A. Chatzinikolaou, A. Mitrakou, G. Mastorakos, I. Papassotiriou, K. Taxildaris, D. Kouretas, Oxidative stress biomarkers responses to physical overtraining: implications for diagnosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 43(6), 901–910 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.05.022
E.I. Germanou, A. Chatzinikolaou, P. Malliou, A. Beneka, A.Z. Jamurtas, C. Bikos, D. Tsoukas, A. Theodorou, I. Katrabasas, K. Margonis, I. Douroudos, A. Gioftsidou, I.G. Fatouros, Oxidative stress and inflammatory responses following an acute bout of isokinetic exercise in obese women with knee osteoarthritis. Knee. 20(6), 581–590 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.knee.2012.10.020
I. Barbas, I.G. Fatouros, Douroudos II, A. Chatzinikolaou, Y. Michailidis, D. Draganidis, A.Z. Jamurtas, M.G. Nikolaidis, C. Parotsidis, A.A. Theodorou, I. Katrabasas, K. Margonis, I. Papassotiriou, K. Taxildaris, Physiological and performance adaptations of elite Greco-Roman wrestlers during a one-day tournament. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 111(7), 1421–1436 (2011). doi:10.1007/s00421-010-1761-7
J. Mi, M.N. Munkonda, M. Li, M.X. Zhang, X.Y. Zhao, P.C. Fouejeu, K. Cianflone, Adiponectin and leptin metabolic biomarkers in chinese children and adolescents. J. Obes. 2010, 892081 (2010). doi:10.1155/2010/892081
A.D. Aygun, S. Gungor, B. Ustundag, M.K. Gurgoze, Y. Sen, Proinflammatory cytokines and leptin are increased in serum of prepubertal obese children. Mediators Inflamm. 2005(3), 180–183 (2005). doi:10.1155/MI.2005.180
A. Jmal, O. Bouyahya, I. Ayadi, H. Occhi, M. Feki, N. Kaabachi, A. Sammoud, M. Abdennebi, S. Boukthir, Serum leptin concentration in Tunisian non obese children. Ann. Biol. Clin. (Paris) 68(3), 311–315 (2010). doi:10.1684/abc.2010.0433
G.A. Martos-Moreno, V. Barrios, J. Argente, Normative data for adiponectin, resistin, interleukin 6, and leptin/receptor ratio in a healthy Spanish pediatric population: relationship with sex steroids. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 155(3), 429–434 (2006). doi:10.1530/eje.1.02227
T. Reinehr, C. Roth, T. Menke, W. Andler, Adiponectin before and after weight loss in obese children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89(8), 3790–3794 (2004). doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031925
R.R. Kraemer, V.D. Castracane, Effect of acute and chronic exercise on ghrelin and adipocytokines during pubertal development. Med. Sport Sci. 55, 156–173 (2010). doi:10.1159/000321979000321979
A.Z. Jamurtas, V. Theocharis, G. Koukoulis, N. Stakias, I.G. Fatouros, D. Kouretas, Y. Koutedakis, The effects of acute exercise on serum adiponectin and resistin levels and their relation to insulin sensitivity in overweight males. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 97(1), 122–126 (2006). doi:10.1007/s00421-006-0169-x
C. Maziere, G. Alimardani, F. Dantin, F. Dubois, M.A. Conte, J.C. Maziere, Oxidized LDL activates STAT1 and STAT3 transcription factors: possible involvement of reactive oxygen species. FEBS Lett. 448(1), 49–52 (1999). doi:S0014-5793(99)00324-5
L. Gong, F. Yuan, J. Teng, X. Li, S. Zheng, L. Lin, H. Deng, G. Ma, C. Sun, Y. Li, Weight loss, inflammatory markers, and improvements of iron status in overweight and obese children. J. Pediatr. 164(4), 795–800 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.12.004
E. Cholez, V. Debuysscher, J. Bourgeais, C. Boudot, J. Leprince, F. Tron, B. Brassart, A. Regnier, E. Bissac, E. Pecnard, F. Gouilleux, K. Lassoued, V. Gouilleux-Gruart, Evidence for a protective role of the STAT5 transcription factor against oxidative stress in human leukemic pre-B cells. Leukemia 26(11), 2390–2397 (2012). doi:10.1038/leu.2012.112
W.S. Hahn, J. Kuzmicic, J.S. Burrill, M.A. Donoghue, R. Foncea, M.D. Jensen, S. Lavandero, E.A. Arriaga, D.A. Bernlohr, Proinflammatory cytokines differentially regulate adipocyte mitochondrial metabolism, oxidative stress, and dynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 306(9), E1033–1045 (2014). doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00422.2013
S. Araki, K. Dobashi, K. Kubo, Y. Yamamoto, K. Asayama, A. Shirahata, N-acetylcysteine attenuates TNF-alpha induced changes in secretion of interleukin-6, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and adiponectin from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Life Sci. 79(25), 2405–2412 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2006.08.004
B. Frossi, M. De Carli, K.C. Daniel, J. Rivera, C. Pucillo, Oxidative stress stimulates IL-4 and IL-6 production in mast cells by an APE/Ref-1-dependent pathway. Eur. J. Immunol. 33(8), 2168–2177 (2003). doi:10.1002/eji.200323995
E.S. Ford, D.A. Galuska, C. Gillespie, J.C. Will, W.H. Giles, W.H. Dietz, C-reactive protein and body mass index in children: findings from the third national health and nutrition examination survey, 1988–1994. J. Pediatr. 138(4), 486–492 (2001). doi:10.1067/mpd.2001.112898
B.H. Lourenco, M.A. Cardoso, C-reactive protein concentration predicts change in body mass index during childhood. PLoS One 9(3), e90357 (2014). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090357
S.V. Galcheva, V.M. Iotova, Y.T. Yotov, S. Bernasconi, M.E. Street, Circulating proinflammatory peptides related to abdominal adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in healthy prepubertal children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 164(4), 553–558 (2011). doi:10.1530/eje-10-1124
H. Liu, Y. Yang, G. Huang, S. Tan, Y. Liu, Positive association of pro-inflammatory biomarkers and increased oxidative stress in the healthy elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 54(2), e8–e12 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.archger.2011.05.016
A. Mohn, D. Marzio, C. Giannini, R. Capanna, M. Marcovecchio, F. Chiarelli, Alterations in the oxidant-antioxidant status in prepubertal children with growth hormone deficiency: effect of growth hormone replacement therapy. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 63(5), 537–542 (2005). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02378.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the parents/guardians of each child, while verbal consent to participate in the study was obtained from all children.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paltoglou, G., Schoina, M., Valsamakis, G. et al. Interrelations among the adipocytokines leptin and adiponectin, oxidative stress and aseptic inflammation markers in pre- and early-pubertal normal-weight and obese boys. Endocrine 55, 925–933 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1227-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1227-3