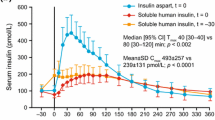
Abstract
Insulin therapy provides effective glycemic control in patients with diabetes who have deficient beta-cell function and insulin secretion. Subjects with type 2 diabetes not adequately controlled on oral agents or incretin therapies can initiate basal insulin replacement to correct fasting hyperglycemia. While all basal insulin preparations have similar efficacy in lowering fasting plasma glucose and improving A1C, the newer basal insulin analogs are associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia than NPH insulin. Patients whose A1C levels remain above goal despite adequate basal insulin replacement need to evaluate and correct post-prandial hyperglycemia. With progressive beta-cell deficiency, rapid-acting insulin preparations can be introduced before one or more meals and titrated to achieve post-prandial glycemic control. For many patients requiring full basal/bolus insulin replacement, a strategy of fixed prandial insulin doses can yield acceptable glycemic control when compared to a more sophisticated approach utilizing carbohydrate counting and matching to insulin. Concentrated insulin preparations such as U-500 have also been of value in patients with resistant type 2 diabetes. Regardless of the type of insulin replacement used, the blood glucose lowering effects of insulin need to be carefully balanced with the increasing risk of hypoglycemia, and the weight gain associated with insulin intensification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.L. Wajchenberg, Beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment. Endocr. Rev. 28(2), 187–218 (2007)
D.M. Nathan, J.B. Buse, M.B. Davidson, E. Ferrannini, R.R. Holman, R. Sherwin, B. Zinman, Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(1), 193–203 (2009)
R.R. Holman, A.J. Farmer, M.J. Davies, J.C. Levy, J.L. Darbyshire, J.F. Keenan, S.K. Paul, Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 361(18), 1736–1747 (2009)
J.S. Skyler, R. Bergenstal, R.O. Bonow, J. Buse, P. Deedwania, E.A. Gale, B.V. Howard, M.S. Kirkman, M. Kosiborod, P. Reaven, R.S. Sherwin, Intensive glycemic control and the prevention of cardiovascular events: implications of the ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VA Diabetes Trials: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a Scientific Statement of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 53(3), 298–304 (2009)
I.B. Hirsch, Insulin analogues. N. Engl. J. Med. 352(2), 174–183 (2005)
P. Kurtzhals, Pharmacology of insulin detemir. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 36(Suppl 1), 14–20 (2007)
H.W. Rodbard, L. Blonde, S.S. Braithwaite, E.M. Brett, R.H. Cobin, Y. Handelsman, R. Hellman, P.S. Jellinger, L.G. Jovanovic, P. Levy, J.I. Mechanick, F. Zangeneh, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for the management of diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Pract. 13(Suppl 1), 1–68 (2007)
American Diabetes Association, Standards of medical care in diabetes–2012. Diabetes Care 35(Suppl 1), S11–S63 (2012)
M.C. Riddle, J. Rosenstock, J. Gerich, The treat-to-target trial: randomized addition of glargine or human NPH insulin to oral therapy of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 26(11), 3080–3086 (2003)
J. Rosenstock, M. Davies, P.D. Home, J. Larsen, C. Koenen, G. Schernthaner, A randomised, 52-week, treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with insulin glargine when administered as add-on to glucose-lowering drugs in insulin-naive people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 51(3), 408–416 (2008)
A. Philis-Tsimikas, Tolerability, safety and adherence to treatment with insulin detemir injection in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2, 323–332 (2008)
M. Lepore, S. Pampanelli, C. Fanelli, F. Porcellati, L. Bartocci, A. Di Vincenzo, C. Cordoni, E. Costa, P. Brunetti, G.B. Bolli, Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of subcutaneous injection of long-acting human insulin analog glargine, NPH insulin, and ultralente human insulin and continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin lispro. Diabetes 49(12), 2142–2148 (2000)
T. Heise, L. Nosek, B.B. Ronn, L. Endahl, L. Heinemann, C. Kapitza, E. Draeger, Lower within-subject variability of insulin detemir in comparison to NPH insulin and insulin glargine in people with Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 53, 1614–1620 (2004)
F. Porcellati, P. Rossetti, N.R. Busciantella, S. Marzotti, P. Lucidi, S. Luzio, D.R. Owens, G.B. Bolli, C.G. Fanelli, Comparison of pharmacokinetics and dynamics of the long-acting insulin analogs glargine and detemir at steady state in type 1 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Diabetes Care 30(10), 2447–2452 (2007)
O. Klein, J. Lynge, L. Endahl, B. Damholt, L. Nosek, T. Heise, Albumin-bound basal insulin analogues (insulin detemir and NN344): comparable time-action profiles but less variability than insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 9(3), 290–299 (2007)
K. Horvath, K. Jeitler, A. Berghold, S.H. Ebrahim, T.W. Gratzer, J. Plank, T. Kaiser, T.R. Pieber, A. Siebenhofer, Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH insulin (human isophane insulin) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2, CD005613 (2007)
S.G. Swinnen, A.C. Simon, F. Holleman, J.B. Hoekstra, J.H. Devries, Insulin detemir versus insulin glargine for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 7, CD006383 (2011)
J. Plank, A. Siebenhofer, A. Berghold, K. Jeitler, K. Horvath, P. Mrak, T.R. Pieber, Systematic review and meta-analysis of short-acting insulin analogues in patients with diabetes mellitus. Arch. Intern. Med. 165(12), 1337–1344 (2005)
P.D. Home, The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rapid-acting insulin analogues and their clinical consequences. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 14(9), 780–788 (2012)
G. Schernthaner, W. Wein, N. Shnawa, P.C. Bates, M.A. Birkett, Preprandial vs. postprandial insulin lispro-a comparative crossover trial in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 21(3), 279–284 (2004)
S.K. Garg, J. Rosenstock, K. Ways, Optimized Basal-bolus insulin regimens in type 1 diabetes: insulin glulisine versus regular human insulin in combination with basal insulin glargine. Endocr. Pract. 11(1), 11–17 (2005)
T. Danne, J. Aman, E. Schober, D. Deiss, J.L. Jacobsen, H.H. Friberg, L.H. Jensen, A comparison of postprandial and preprandial administration of insulin aspart in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(8), 2359–2364 (2003)
M. Gagnon-Auger, P. du Souich, J.P. Baillargeon, E. Martin, P. Brassard, J. Menard, J.L. Ardilouze, Dose-dependent delay of the hypoglycemic effect of short-acting insulin analogs in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study. Diabetes Care 33(12), 2502–2507 (2010)
Y. Handelsman, J.I. Mechanick, L. Blonde, G. Grunberger, Z.T. Bloomgarden, G.A. Bray, S. Dagogo-Jack, J.A. Davidson, D. Einhorn, O. Ganda, A.J. Garber, I.B. Hirsch, E.S. Horton, F. Ismail-Beigi, P.S. Jellinger, K.L. Jones, L. Jovanovic, H. Lebovitz, P. Levy, E.S. Moghissi, E.A. Orzeck, A.I. Vinik, K.L. Wyne, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan. Endocr. Pract. 17(Suppl 2), 1–53 (2011)
S.E. Inzucchi, R.M. Bergenstal, J.B. Buse, M. Diamant, E. Ferrannini, M. Nauck, A.L. Peters, A. Tsapas, R. Wender, D.R. Matthews, Management of hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Diabetes Care 35(6), 1364–1379 (2012)
R.R. Holman, K.I. Thorne, A.J. Farmer, M.J. Davies, J.F. Keenan, S. Paul, J.C. Levy, Addition of biphasic, prandial, or basal insulin to oral therapy in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 357(17), 1716–1730 (2007)
A. Philis-Tsimikas, G. Charpentier, P. Clauson, G.M. Ravn, V.L. Roberts, B. Thorsteinsson, Comparison of once-daily insulin detemir with NPH insulin added to a regimen of oral antidiabetic drugs in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. Clin. Ther. 28(10), 1569–1581 (2006)
M. Davies, F. Storms, S. Shutler, M. Bianchi-Biscay, R. Gomis, Improvement of glycemic control in subjects with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes: comparison of two treatment algorithms using insulin glargine. Diabetes Care 28(6), 1282–1288 (2005)
L. Blonde, M. Merilainen, V. Karwe, P. Raskin, Patient-directed titration for achieving glycaemic goals using a once-daily basal insulin analogue: an assessment of two different fasting plasma glucose targets—the TITRATE study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 11(6), 623–631 (2009)
L. Meneghini, C. Koenen, W. Weng, J.L. Selam, The usage of a simplified self-titration dosing guideline (303 Algorithm) for insulin detemir in patients with type 2 diabetes–results of the randomized, controlled PREDICTIVE 303 study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 9(6), 902–913 (2007)
A. Fritsche, M.A. Schweitzer, H.U. Haring, Glimepiride combined with morning insulin glargine, bedtime neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin, or bedtime insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 138(12), 952–959 (2003)
H. Yokoyama, J. Tada, F. Kamikawa, S. Kanno, Y. Yokota, M. Kuramitsu, Efficacy of conversion from bedtime NPH insulin to morning insulin glargine in type 2 diabetic patients on basal-prandial insulin therapy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 73(1), 35–40 (2006)
H.U. Janka, G. Plewe, K. Busch, Combination of oral antidiabetic agents with basal insulin versus premixed insulin alone in randomized elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 55(2), 182–188 (2007)
H.U. Janka, G. Plewe, M.C. Riddle, C. Kliebe-Frisch, M.A. Schweitzer, H. Yki-Jarvinen, Comparison of basal insulin added to oral agents versus twice-daily premixed insulin as initial insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28(2), 254–259 (2005)
A.H. Barnett, B. Charbonnel, M. Donovan, D. Fleming, R. Chen, Effect of saxagliptin as add-on therapy in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes on insulin alone or insulin combined with metformin. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 28(4), 513–523 (2012)
T. Vilsboll, J. Rosenstock, H. Yki-Jarvinen, W.T. Cefalu, Y. Chen, E. Luo, B. Musser, P.J. Andryuk, Y. Ling, K.D. Kaufman, J.M. Amatruda, S.S. Engel, L. Katz, Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 12(2), 167–177 (2010)
M. Riddle, R. Pencek, S. Charenkavanich, K. Lutz, K. Wilhelm, L. Porter, Randomized comparison of pramlintide or mealtime insulin added to basal insulin treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(9), 1577–1582 (2009)
P.A. Levin, J.H. Mersey, S. Zhou, L.A. Bromberger, Clinical outcomes using long-term combination therapy with insulin glargine and exenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Pract. 18(1), 17–25 (2012)
J.B. Buse, R.M. Bergenstal, L.C. Glass, C.R. Heilmann, M.S. Lewis, A.Y. Kwan, B.J. Hoogwerf, J. Rosenstock, Use of twice-daily exenatide in basal insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 154(2), 103–112 (2011)
P. Raskin, E. Allen, P. Hollander, A. Lewin, R.A. Gabbay, P. Hu, B. Bode, A. Garber, Initiating insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a comparison of biphasic and basal insulin analogs. Diabetes Care 28(2), 260–265 (2005)
J. Rosenstock, A.J. Ahmann, G. Colon, J. Scism-Bacon, H. Jiang, S. Martin, Advancing insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes previously treated with glargine plus oral agents: prandial premixed (insulin lispro protamine suspension/lispro) versus basal/bolus (glargine/lispro) therapy. Diabetes Care 31(1), 20–25 (2008)
A. Liebl, R. Prager, K. Binz, M. Kaiser, R. Bergenstal, B. Gallwitz, Comparison of insulin analogue regimens in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the PREFER study: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 11(1), 45–52 (2009)
L. Meneghini, H. Mersebach, S. Kumar, A.L. Svendsen, K. Hermansen, Comparison of 2 intensification regimens with rapid-acting insulin aspart in type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by once-daily insulin detemir and oral antidiabetes drugs: the step-wise randomized study. Endocr. Pract. 17(5), 727–736 (2011)
M.R. Lankisch, K.C. Ferlinz, J.L. Leahy, W.A. Scherbaum, Introducing a simplified approach to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a comparison of two single-dose regimens of insulin glulisine plus insulin glargine and oral antidiabetic drugs. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 10(12), 1178–1185 (2008)
M.B. Davidson, P. Raskin, R.J. Tanenberg, A. Vlajnic, P. Hollander, A stepwise approach to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes failing basal insulin treatment. Endocr. Pract. 17(3), 395–405 (2011)
I.B. Hirsch, R.M. Bergenstal, C.G. Parkin, E. Wright, J.B. Buse, A real-world approach to insulin therapy in primary care practice. Clin. Diabetes 23(2), 78–86 (2005)
L.F. Meneghini, K. Hermansen, H. Mersebach, A.L. Svendsen, S. Kumar, Treatment in-tensification by stepwise addition of prandial insulin aspart to once-daily basal insulin detemir in subjects with type 2 diabetes: the STEPwise™ trial. Diabetes 59(Supplement 1), A199 (2010)
R.M. Bergenstal, M. Johnson, M.A. Powers, A. Wynne, A. Vlajnic, P. Hollander, M. Rendell, Adjust to target in type 2 diabetes: comparison of a simple algorithm with carbohydrate counting for adjustment of mealtime insulin glulisine. Diabetes Care 31(7), 1305–1310 (2008)
A. de la Pena, M. Riddle, L.A. Morrow, H.H. Jiang, H. Linnebjerg, A. Scott, K.M. Win, M. Hompesch, K.F. Mace, J.G. Jacobson, J.A. Jackson, Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of high-dose human regular U-500 insulin versus human regular U-100 insulin in healthy obese subjects. Diabetes Care 34(12), 2496–2501 (2011)
S.L. Quinn, M.C. Lansang, D. Mina, Safety and effectiveness of U-500 insulin therapy in patients with insulin-resistant type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy 31(7), 695–702 (2011)
W.S. Wafa, M.I. Khan, Use of U-500 regular insulin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29(9), 2175–2176 (2006)
P. Ballani, M.T. Tran, M.D. Navar, M.B. Davidson, Clinical experience with U-500 regular insulin in obese, markedly insulin-resistant type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 29(11), 2504–2505 (2006)
J.M. Neal, Analysis of effectiveness of human U-500 insulin in patients unresponsive to conventional insulin therapy. Endocr. Pract. 11(5), 305–307 (2005)
UK Hypoglycemia Study Group, Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia 50(6), 1140–1147 (2007)
H.C. Gerstein, M.E. Miller, R.P. Byington, D.C. Goff Jr, J.T. Bigger, J.B. Buse, W.C. Cushman, S. Genuth, F. Ismail-Beigi, R.H. Grimm Jr, J.L. Probstfield, D.G. Simons-Morton, W.T. Friedewald, Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 358(24), 2545–2559 (2008)
W. Duckworth, C. Abraira, T. Moritz, D. Reda, N. Emanuele, P.D. Reaven, F.J. Zieve, J. Marks, S.N. Davis, R. Hayward, S.R. Warren, S. Goldman, M. McCarren, M.E. Vitek, W.G. Henderson, G.D. Huang, Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 360(2), 129–139 (2009)
M.C. Riddle, W.T. Ambrosius, D.J. Brillon, J.B. Buse, R.P. Byington, R.M. Cohen, D.C. Goff Jr, S. Malozowski, K.L. Margolis, J.L. Probstfield, A. Schnall, E.R. Seaquist, Epidemiologic relationships between A1C and all-cause mortality during a median 3.4-year follow-up of glycemic treatment in the ACCORD trial. Diabetes Care 33(5), 983–990 (2010)
M.E. Miller, D.E. Bonds, H.C. Gerstein, E.R. Seaquist, R.M. Bergenstal, J. Calles-Escandon, R.D. Childress, T.E. Craven, R.M. Cuddihy, G. Dailey, M.N. Feinglos, F. Ismail-Beigi, J.F. Largay, P.J. O’Connor, T. Paul, P.J. Savage, U.K. Schubart, A. Sood, S. Genuth, The effects of baseline characteristics, glycaemia treatment approach, and glycated haemoglobin concentration on the risk of severe hypoglycaemia: post hoc epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ 340, b5444 (2010)
J.S. Skyler, R. Bergenstal, R.O. Bonow, J. Buse, P. Deedwania, E.A. Gale, B.V. Howard, M.S. Kirkman, M. Kosiborod, P. Reaven, R.S. Sherwin, Intensive glycemic control and the prevention of cardiovascular events: implications of the ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VA diabetes trials: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a scientific statement of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association. Diabetes Care 32(1), 187–192 (2009)
S. Zoungas, J. Chalmers, T. Ninomiya, Q. Li, M.E. Cooper, S. Colagiuri, G. Fulcher, B.E. de Galan, S. Harrap, P. Hamet, S. Heller, S. Macmahon, M. Marre, N. Poulter, F. Travert, A. Patel, B. Neal, M. Woodward, Association of HbA1c levels with vascular complications and death in patients with type 2 diabetes: evidence of glycaemic thresholds. Diabetologia 55(3), 636–643 (2012)
L.F. Meneghini, B. Miranda-Palma, Insulin degludec: a novel ultra-long-acting basal insulin for use in Type 1 and 2 diabetes. Expert Rev. Endocr. Metab. 7(1), 9–14 (2012)
Disclosure
L. Meneghini is on the Advisory Board/Panel of Novo Nordisk; he is also the Consultant for Novo Nordisk and sanofi-aventis. Grant/Research Support were provided by MannKind, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meneghini, L.F. Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 43, 529–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9817-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9817-6