Abstract
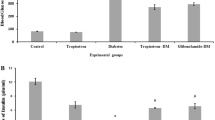
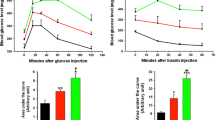
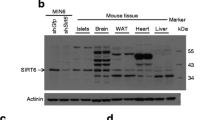
Increasing evidence suggests that a restricted caloric intake extends the life span of mammals, and SIRT1 may play a key role in this process. To study the effects of caloric restriction on SIRT1 expression and apoptosis of islet beta cells in type 2 diabetic rats, we first induced a model of type 2 diabetes in rats with a low-dose of streptozotocin. Then, the rats were fed with a normal diet, high-fat diet or 60% caloric restriction, respectively. As a result, the apoptosis ratio of islet beta cells in diabetic rats was dramatically increased compared to the control group, and mRNA and protein expression of SIRT1 in islet beta cells were much lower than those of the control group. After caloric restriction for 1 month, the blood glucose and serum insulin of rats decreased. The mRNA and protein expression of SIRT1 in islet beta cells significantly increased; however, the apoptosis ratio of islet beta cells decreased remarkably. These data show that caloric restriction notably improves the sensitivity to insulin and significantly increases mRNA and protein expression of SIRT1 while decreasing the apoptosis ratio of islet beta cells in diabetic rats. Therefore, SIRT1 may play an important role in the apoptosis of islet beta cells of type 2 diabetes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donath MY, Halban PA (2004) Decreased β-cell mass in diabetes: significance, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Diabetologia 47:581–589
Rhodes CJ (2005) Type 2 diabetes–a matter of β-cell life and death? Science 307:380–384
Guarente L, Picard F (2005) Calorie restriction—the SIR2 connection. Cell 120:473–482
Leibiger IB, Berggren PO (2006) Sirt1: a metabolic master switch that modulates lifespan. Nat Med 12:34–36
Moynihan KA, Grimm AA, Plueger MM et al (2005) Increased dosage of mammalian Sir2 in pancreatic beta cells enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. Cell Metab 2:105–117
Bordone L, Motta MC, Picard F et al (2006) Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion by repressing UCP2 in pancreatic b cells. PLoS Biol 4:e31
Lerco MM, Macedo CS, Silva RJ et al (2006) The number of podocyte and slit diaphragm is decreased in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Acta Cir Bras 21:87–91
Ugochukwu NH, Bagayoko ND, Antwi ME (2004) The effects of dietary caloric restriction on antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in mild and severe streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Clin Chim Acta 348:121–129
Cui YF, Ma M, Wang GY et al (2005) Prevention of core cell damage in isolated islets of Langerhans by low temperature preconditioning. World J Gastroenterol 11:545–550
Sigfrid LA, Cunningham JM, Beeharry N et al (2004) Antioxidant enzyme activity and mRNA expression in the islets of Langerhans from the BB/S rat model of type 1 diabetes and an insulin-producing cell line. J Mol Med 82:325–335
Mabley JG, Belin VD, John NE et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor 1 reverses interleukin-1b inhibition of insulin secretion, induction of nitric oxide synthase and cytokinemediated apoptosis in rat islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett 417:235–238
Wang H, Kouri G, Wollheim CB (2005) ER stress and SREBP-1 activation are implicated in beta cells glucolipotoxicity. J Cell Sci 118:3905–3915
Winzell MS, Holm C, Ahren B (2003) Downregulation of islet hormone-sensitive lipase during long-term high-fat feeding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304:273–278
Striffler JS, Nadler JL (2004) Lisofylline, a novel anti-inflammatory agent, enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in vivo and in vitro: studies in prediabetic and normal rats. Metabolism 53:290–296
Wetter TJ, Gazdag AC, Dean DJ et al (1999) Effect of calorie restriction on in vivo glucose metabolism by individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol 276:E728–E738
McCurdy CE, Davidson RT, Cartee GD (2003) Brief calorie restriction increases Akt2 phosphorylation in insulin-stimulated rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E693–E700
Roth GS, Lane MA, Ingram DK (2005) Caloric restriction mimetics: the next phase. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1057:365–371
Koubova J, Guarente L (2003) How does calorie restriction work? Genes Dev 17:313–321
Bitterman KJ, Anderson RM, Cohen HY et al (2002) Inhibition of silencing and accelerated aging by nicotinamide, a putative negative regulator of yeast Sir2 and human SIRT1. J Biol Chem 277:45099–45107
Lamming DW, Wood JG, Sinclair DA (2004) Small molecules that regulate lifespan: evidence for xenohormesis. Mol Microbiol 53:1003–1009
Pagans S, Pedal A, North BJ et al (2005) SIRT1 regulates HIV transcription via Tat deacetylation. PLoS Biol 3:210–220
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF et al (2004) Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303:2011–2015
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S et al (2001) Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell 107:137–148
Cohen HY, Miller C, Bitterman KJ et al (2004) Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 305:390–392
Hui H, Dotta F, Di Mario U et al (2004) Role of caspases in the regulation of apoptotic pancreatic islet beta-cells death. J Cell Physiol 200:177–200
Lowell BB, Shulman GI (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science 307:384–387
Mathis D, Vence C, Benoist C (2001) Beta-cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature 414:792–798
Sun C, Zhang F, Ge X et al (2007) SIRT1 improves insulin sensitivity under insulin-resistant conditions by repressing PTP1B. Cell Metab 6:307–319
Lee JH, Song MY, Song EK et al (2009) Overexpression of SIRT1 protects pancreatic beta-cells against cytokine toxicity by suppressing the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Diabetes 58:344–351
Pickup JC (2004) Inflammation and activated innate immunity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27:813–823
Donath MY, Schumann DM, Faulenbach M et al (2008) Islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes: from metabolic stress to therapy. Diabetes Care 31(2):S161–S164
Milne JC, Lambert PD, Schenk S et al (2007) Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature 450:712–716
Acknowledgments
The technical assistance of Yan Li and Yuan Tian is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, X., Cheng, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of caloric restriction on SIRT1 expression and apoptosis of islet beta cells in type 2 diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol 47 (Suppl 1), 177–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0159-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0159-7